Page 428 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 428
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
424 Chapter 11: Endocrine system
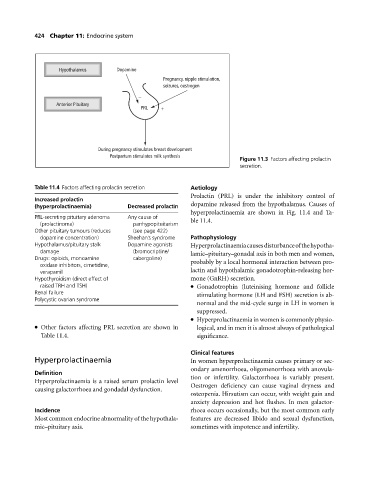
Hypothalamus Dopamine
Pregnancy, nipple stimulation,
seizures, oestrogen
−
Anterior Pituitary
PRL +
During pregnancy stimulates breast development
Postpartum stimulates milk synthesis
Figure 11.3 Factors affecting prolactin
secretion.
Table 11.4 Factors affecting prolactin secretion Aetiology
Prolactin (PRL) is under the inhibitory control of
Increased prolactin
(hyperprolactinaemia) Decreased prolactin dopamine released from the hypothalamus. Causes of
hyperprolactinaemia are shown in Fig. 11.4 and Ta-
PRL-secreting pituitary adenoma Any cause of ble 11.4.
(prolactinoma) panhypopituitarism
Other pituitary tumours (reduces (see page 422)
dopamine concentration) Sheehan’s syndrome Pathophysiology
Hypothalamus/pituitary stalk Dopamine agonists Hyperprolactinaemiacausesdisturbanceofthehypotha-
damage (bromocriptine/ lamic–pituitary–gonadal axis in both men and women,
Drugs: opioids, monoamine cabergoline) probably by a local hormonal interaction between pro-
oxidase inhibitors, cimetidine,
verapamil lactin and hypothalamic gonadotrophin-releasing hor-
Hypothyroidism (direct effect of mone (GnRH) secretion.
raised TRH and TSH) Gonadotrophin (luteinising hormone and follicle
Renal failure stimulating hormone (LH and FSH) secretion is ab-
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
normal and the mid-cycle surge in LH in women is
suppressed.
Hyperprolactinaemia in women is commonly physio-
Other factors affecting PRL secretion are shown in logical, and in men it is almost always of pathological
Table 11.4. significance.
Clinical features
Hyperprolactinaemia In women hyperprolactinaemia causes primary or sec-
ondary amenorrhoea, oligomenorrhoea with anovula-
Definition
tion or infertility. Galactorrhoea is variably present.
Hyperprolactinaemia is a raised serum prolactin level
Oestrogen deficiency can cause vaginal dryness and
causing galactorrhoea and gondadal dysfunction.
osteopenia. Hirsutism can occur, with weight gain and
anxiety depression and hot flushes. In men galactor-
Incidence rhoea occurs occasionally, but the most common early
Most common endocrine abnormality of the hypothala- features are decreased libido and sexual dysfunction,
mic–pituitary axis. sometimes with impotence and infertility.