Page 430 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 430
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
426 Chapter 11: Endocrine system
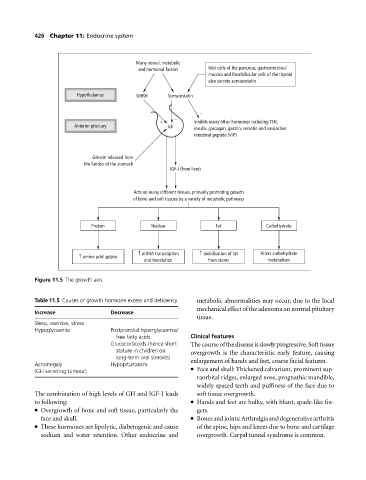
Many neural, metabolic
and hormonal factors Islet cells of the pancreas, gastrointestinal
mucosa and Parafollicular cells of the thyroid
also secrete somatostatin
Hypothalamus GHRH Somatostatin
−
−
+ Inhibits many other hormones including TSH,
Anterior pituitary GH insulin, glucagon, gastrin, secretin and vasoactive
intestinal peptide (VIP)
GHrelin released from
the fundus of the stomach
IGF-I (from liver)
Acts on many different tissues, primarily promoting growth
of bone and soft tissues by a variety of metabolic pathways
Protein Nuclear Fat Carbohydrate
↑ mRNA transcription ↑ mobilisation of fat Alters carbohydrate
↑ amino acid uptake
and translation from stores metabolism
Figure 11.5 The growth axis.
Table 11.5 Causes of growth hormone excess and deficiency metabolic abnormalities may occur, due to the local
mechanical effect of the adenoma on normal pituitary
Increase Decrease
tissue.
Sleep, exercise, stress
Hypoglycaemia Postprandial hyperglycaemia/
free fatty acids Clinical features
Glucocorticoids (hence short The course of the disease is slowly progressive. Soft tissue
stature in children on overgrowth is the characteristic early feature, causing
long-term oral steroids)
Acromegaly Hypopituitarism enlargement of hands and feet, coarse facial features.
Face and skull: Thickened calvarium, prominent sup-
(GH secreting tumour)
raorbital ridges, enlarged nose, prognathic mandible,
widely spaced teeth and puffiness of the face due to
The combination of high levels of GH and IGF-I leads soft tissue overgrowth.
to following: Hands and feet are bulky, with blunt, spade-like fin-
Overgrowth of bone and soft tissue, particularly the gers.
face and skull. Bonesandjoints:Arthralgiaanddegenerativearthritis
These hormones are lipolytic, diabetogenic and cause of the spine, hips and knees due to bone and cartilage
sodium and water retention. Other endocrine and overgrowth. Carpal tunnel syndrome is common.