Page 130 - Science
P. 130
RESEARCH | REPORT
worm burdens compared to control Il7r cre/+ mice ing the intestine. Adrb2 −/− mice exhibited increased ited similar expression levels of genes encoding
(Fig. 2, N and O). b 2 AR agonist treatment of frequencies of ILC2s in the lung compared to ILC2-associated transcription factors (Id2, Gata3,
Il7r cre/+ Adrb2 f/f mice did not induce significant Adrb2 +/+ mice after infection (Fig. 3A). As an ad- and Rora)and cytokine receptors (Il1rl1, Crlf2,and
changes in eosinophilia and worm burden after ditional approach to induce lung inflammation, Il4ra) (Fig. 4A), we also observed significant down-
helminth infection (fig. S2, M and N). Further- we administered the alarmin IL-33 intranasally regulation of a number of genes in the agonist-
more, irradiated Adrb2 +/+ and Adrb2 −/− mice and observed increased frequencies of ILC2s treated groups compared to that in controls. Gene
reconstituted with Adrb2 +/+ BM cells had sim- in Adrb2 −/− mice compared to that in Adrb2 +/+ set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the down-
ilar worm burdens after helminth infection (fig. mice (Fig. 3B). Further, ILC2 frequencies and regulated genes revealed significant enrichment
S2O). These results indicate that b 2 AR signal- cytokine production after IL-33 administration in gene ontology (GO) terms associated with the
ing on CD127 (IL-7 receptor a,IL-7Ra)–expressing were inhibited by b 2 AR agonist treatment (Fig. 3, cell cycle and cell proliferation (Fig. 4, B and C,
–
CD4 hematopoietic cells, including ILC2s, is C and D). Similarly, when the mice received ex- and fig. S3A). Taken together with the reduced
important during anti-helminth responses but tract of the fungal allergen Alternaria alternata ILC2 numbers observed in these mice after in-
not essential for radio-resistant cells and CD127- intranasally, b 2 AR agonist–treated mice had re- fection (Fig. 2F), these results collectively sug-
negative cells. duced frequencies of ILC2s in the lungs than gest a role for b 2 AR signaling in limiting the
To further address the importance of b 2 AR did vehicle-treated mice (Fig. 3E). In addition, proliferation and accumulation of ILC2s.
signaling directly on ILC2s, we reconstituted Il7r cre/+ Adrb2 f/f mice exhibited increased ILC2 To directly test whether b 2 AR signaling reg-
ILC-deficient Rag2 −/− Il2rg −/− mice with Adrb2 +/+ frequencies and cytokine production compared ulates ILC2 proliferation in vivo, we analyzed
or Adrb2 −/− ILC2s by transferring ILC2Ps from to Il7r cre/+ mice after the Alternaria extract ad- the expression of the proliferation marker Ki67
Adrb2 +/+ or Adrb2 −/− mice and then infecting ministration together with anti-CD4 mAb treat- during N. brasiliensis infection in mice treated
themicewith N. brasiliensis.After 7daysofin- ment (Fig. 3, F and G). Collectively, these results with the b 2 AR agonist. After treatment, ILC2s from
fection, there was a trend toward increased SI indicate that b 2 AR signaling is an evolutionarily these mice exhibited reduced frequencies of Ki67-
ILC2s, and we observed increased eosinophilia conserved regulatory pathway serving to dampen expressing ILC2s, but comparable frequencies
in Adrb2 −/− ILC2–reconstituted mice compared to ILC2 responses against diverse inflammatory of apoptotic ILC2s, compared to those of vehicle-
Adrb2 +/+ IL7C2–reconstituted mice (Fig. 2, P and stimuli at multiple mucosal barrier surfaces. treated control mice after infection (Fig. 4D and
Q), further supporting the importance of b 2 AR These data provoke the hypothesis that the fig. S3B), suggesting that b 2 AR stimulation sup- Downloaded from
on ILC2s in controlling anti-helminth responses. signaling through b 2 AR on ILC2s negatively presses ILC2 proliferation but does not regulate
Because lung ILC2s exhibited high levels of regulates ILC2 responses and type 2 inflam- apoptosis. Further, this regulation was not re-
Adrb2 mRNA expression (Fig. 1B) and lung mation after exposure to helminth infection and stricted to N. brasiliensis, because it was also
tissue is also highly innervated (15, 19), we ex- allergens. To investigate the mechanisms under- observed after infection with another gastro-
amined if b 2 AR signaling controls ILC2 responses lying this effect, we performed RNA-seq analy- intestinal helminth, Heligmosomoides polygyrus
in the lung as it does in the intestine. After ino- sis on ILC2s sorted from N. brasiliensis–infected bakeri (Fig.4E).Inaddition, when Adrb2 +/+ and
culation, N. brasiliensis larvae migrate to and Adrb2 +/+ mice with or without b 2 AR agonist treat- Adrb2 −/− mice were injected with IL-33 intrape-
+
induceinflammation in thelungbeforereach- ment. Although ILC2s from both groups exhib- ritoneally, the frequencies of Ki67 ILC2s were http://science.sciencemag.org/
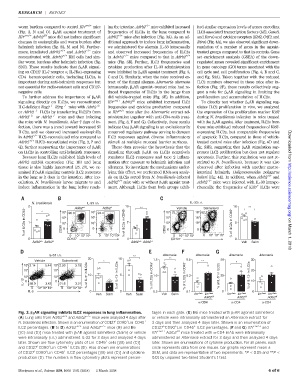
N. brasiliensis IL-33 i.n. IL-33 i.n.
2 * 10 5 90.9 Adrb2 +/+ 10 5 94.4 Adrb2 -/- 10 ** 10 5 75.7 Vehicle 10 5 62.2 10 **
Salmeterol
% of ILC2s in CD45 + 1 10 0 4 3 10 0 4 3 % of ILC2s in CD45 + 7 10 0 4 3 10 0 4 3 % of ILC2s in CD45 + 5
10
10
10
10
CD90
CD90
3
4
0
3
4
3
3
4
4
0
0 CD127 10 10 10 5 0 10 10 10 5 4 CD127 10 10 10 5 0 10 10 10 5 0 on March 1, 2018
Adrb2 +/+ Adrb2 -/- Adrb2 +/+ Adrb2 -/- Veh Salm
Alternaria Alternaria Alternaria Alternaria
**
20 10 **
Vehicle Salmeterol * 1.5 0.5 ** 50 * 30
10 5 3.14 5.44 10 5 2.20 3.18
10 4 10 4 10 5 20
IL-13 10 0 3 88.0 3.42 10 0 3 91.6 3.01 % of IL-5 + in ILC2s % of IL-13 + in ILC2s % of ILC2s in CD45 + 1.0 % of ILC2s in CD45 + 0.3 % of IL-5 + in ILC2s 25 % of IL-13 + in ILC2s 10
3
4
4
3
0 10 10 10 5 0 10 10 10 5
IL-5 0 0 0.5 0.1 0 0
Veh Salm Veh Salm Veh Salm Il7r Cre/+ Il7r Cre/+ Il7r Cre/+ Il7r Cre/+ Il7r Cre/+ Il7r Cre/+
Adrb2 f/f Adrb2 f/f Adrb2 f/f
α-CD4 α-CD4 α-CD4
Fig. 3. b 2 AR signaling inhibits ILC2 responses in lung inflammation. tages in each gate. (E) B6 mice treated with b 2 AR agonist salmeterol
(A) Lung cells from Adrb2 +/+ and Adrb2 −/− mice were analyzed 4 days after or vehicle were intranasally administered an Alternaria extract for
+
+
–
N. brasiliensis infection. Shown is an enumeration of CD127 CD90 Lin CD45 + 3 days and then analyzed 4 days later. Shown is an enumeration of
+
–
+
+
ILC2 percentages. (B to D) Adrb2 +/+ and Adrb2 −/− mice (B) and B6 CD127 CD90 Lin CD45 ILC2 percentages. (F and G) Il7r cre/+ and
[(C) and (D)] mice treated with b 2 AR agonist salmeterol (Salm) or vehicle Il7r cre/+ Adrb2 f/f mice treated with a-CD4 mAb were intranasally
were intranasally (i.n.) administered IL-33 for 3 days and analyzed 4 days administered an Alternaria extract for 3 days and then analyzed 4 days
–
+
later. Shown are flow cytometry plots of Lin CD45 cells [(B) and (C)] later. Shown are enumerations of cytokine production. For all panels, each
+
+
–
+
and CD127 CD90 Lin CD45 ILC2s (D). Also shown are enumerations circle represents data from one mouse, bar graphs represent mean ±
+
+
–
+
of CD127 CD90 Lin CD45 ILC2 percentages [(B) and (C)] and cytokine SEM, and data are representative of two experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P <
production (D). The numbers in flow cytometry plots represent percen- 0.01 by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test.
Moriyama et al., Science 359, 1056–1061 (2018) 2 March 2018 4of6