Page 39 - CASA Bulletin of Anesthesiology 2019 Issue 6
P. 39
Vol.6, No.6, 2019
DOI: 10.31480/2330-4871/104
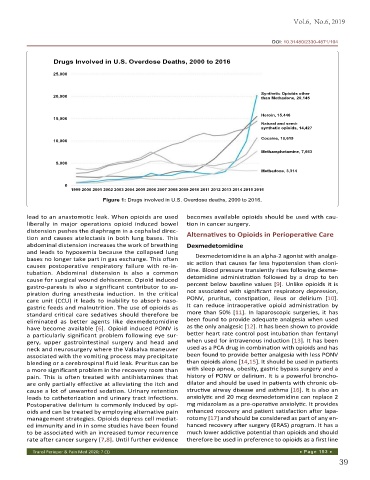
Drugs Involved in U.S. Overdose Deaths, 2000 to 2016
25,000
Synthetic Opioids other
20,000 than Methadone, 20,145
Heroin, 15,446
15,000
Natural and semi-
synthetic opioids, 14,427
Cocaine, 10,619
10,000
Methamphetamine, 7,663
5,000
Methadone, 3,314
0
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
Figure 1: Drugs involved in U.S. Overdose deaths, 2000 to 2016.
lead to an anastomotic leak. When opioids are used becomes available opioids should be used with cau-
liberally in major operations opioid induced bowel tion in cancer surgery.
distension pushes the diaphragm in a cephalad direc- Alternatives to Opioids in Perioperative Care
tion and causes atelectasis in both lung bases. This
abdominal distension increases the work of breathing Dexmedetomidine
and leads to hypoxemia because the collapsed lung Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 agonist with analge-
bases no longer take part in gas exchange. This often
causes postoperative respiratory failure with re-in- sic action that causes far less hypotension than cloni-
tubation. Abdominal distension is also a common dine. Blood pressure transiently rises following dexme-
cause for surgical wound dehiscence. Opioid induced detomidine administration followed by a drop to ten
gastro-paresis is also a significant contributor to as- percent below baseline values [9]. Unlike opioids it is
piration during anesthesia induction. In the critical not associated with significant respiratory depression,
care unit (CCU) it leads to inability to absorb naso- PONV, pruritus, constipation, ileus or delirium [10].
gastric feeds and malnutrition. The use of opioids as It can reduce intraoperative opioid administration by
standard critical care sedatives should therefore be more than 50% [11]. In laparoscopic surgeries, it has
eliminated as better agents like dexmedetomidine been found to provide adequate analgesia when used
have become available [6]. Opioid induced PONV is as the only analgesic [12]. It has been shown to provide
a particularly significant problem following eye sur- better heart rate control post intubation than fentanyl
gery, upper gastrointestinal surgery and head and when used for intravenous induction [13]. It has been
neck and neurosurgery where the Valsalva maneuver used as a PCA drug in combination with opioids and has
associated with the vomiting process may precipitate been found to provide better analgesia with less PONV
bleeding or a cerebrospinal fluid leak. Pruritus can be than opioids alone [14,15]. It should be used in patients
a more significant problem in the recovery room than with sleep apnea, obesity, gastric bypass surgery and a
pain. This is often treated with antihistamines that history of PONV or delirium. It is a powerful broncho-
are only partially effective at alleviating the itch and dilator and should be used in patients with chronic ob-
cause a lot of unwanted sedation. Urinary retention structive airway disease and asthma [16]. It is also an
leads to catheterization and urinary tract infections. anxiolytic and 20 mcg dexmedetomidine can replace 2
Postoperative delirium is commonly induced by opi- mg midazolam as a pre-operative anxiolytic. It provides
oids and can be treated by employing alternative pain enhanced recovery and patient satisfaction after lapa-
management strategies. Opioids depress cell mediat- rotomy [17] and should be considered as part of any en-
ed immunity and in in some studies have been found hanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program. It has a
to be associated with an increased tumor recurrence much lower addictive potential than opioids and should
rate after cancer surgery [7,8]. Until further evidence therefore be used in preference to opioids as a first line
Transl Perioper & Pain Med 2020; 7 (1) • Page 153 •
39