Page 611 - ACFE Fraud Reports 2009_2020
P. 611
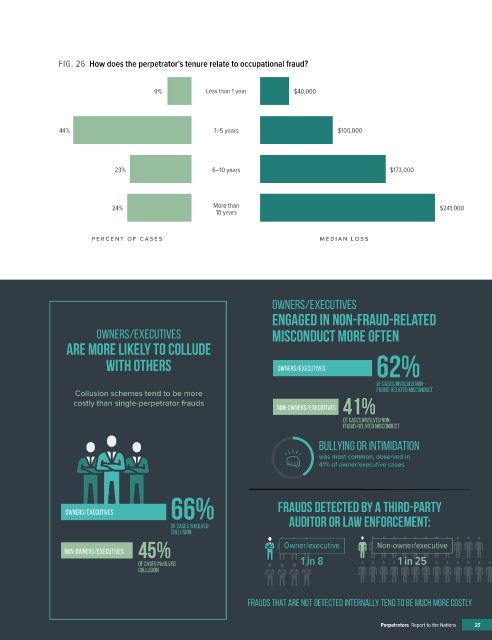
FIG. 26 How does the perpetrator’s tenure relate to occupational fraud?
9% Less than 1 year $40,000
44% 1–5 years $100,000
23% 6–10 years $173,000
24% More than $241,000
10 years
PERCENT OF C A SES MEDIAN L OSS
Owners/executives
FRAUD COMMITTED BY OWNERS AND EXECUTIVES engaged in non-fraud-related
Owners/executives misconduct more often
are more likely to collude
Occupational frauds committed by owners/executives tend to be extremely
costly. How do these cases di er from non-owner/executive frauds? with others owners/executives 62%
of cases involved non-
+
Collusion schemes tend to be more fraud-related misconduct
65% of cases involved non-
MEDIAN LOSS costly than single-perpetrator frauds non-owners/executives 41%
6241
of owner/executive fraud-related misconduct
$850,000 frauds involved � � � � � bullying or intimidation
OWNERS/EXECUTIVES corruption was most common, observed in
41% of owner/executive cases
27%
of owner/executive 66% Frauds detected by a third-party
frauds involved financial owners/executives
statement fraud of cases involved auditor or law enforcement:
collusion
+
34% 6% non-owners/executives 45% Owner/executive Non-owner/executive
Non-ownerS/executives Non-ownerS/executives 1 in 8 1 in 25
$100,000 of cases involved
6645
NONOWNERS/ collusion
EXECUTIVES
Corruption and financial statement fraud are the
two costliest forms of occupational fraud Frauds that are not detected internally tend to be much more costly
Perpetrators Report to the Nations 35