Page 2454 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2454
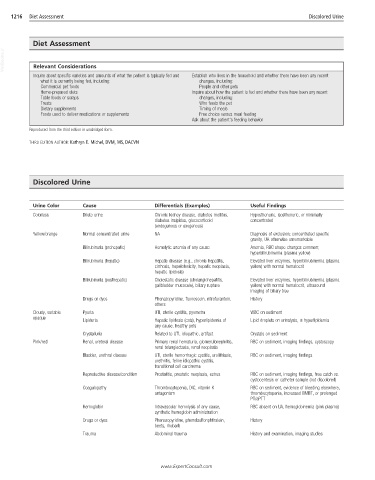
1216 Diet Assessment Discolored Urine
Diet Assessment
VetBooks.ir Relevant Considerations
Inquire about specific varieties and amounts of what the patient is typically fed and Establish who lives in the household and whether there have been any recent
what it is currently being fed, including: changes, including:
Commercial pet foods People and other pets
Home-prepared diets Inquire about how the patient is fed and whether there have been any recent
Table foods or scraps changes, including:
Treats Who feeds the pet
Dietary supplements Timing of meals
Foods used to deliver medications or supplements Free choice versus meal feeding
Ask about the patient’s feeding behavior
Reproduced from the third edition in unabridged form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Kathryn E. Michel, DVM, MS, DACVN
Discolored Urine
Urine Color Cause Differentials (Examples) Useful Findings
Colorless Dilute urine Chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, Hyposthenuric, isosthenuric, or minimally
diabetes insipidus, glucocorticoid concentrated
(endogenous or exogenous)
Yellow/orange Normal concentrated urine NA Diagnosis of exclusion; concentrated specific
gravity, UA otherwise unremarkable
Bilirubinuria (prehepatic) Hemolytic anemia of any cause Anemia, RBC shape changes common;
hyperbilirubinemia (plasma yellow)
Bilirubinuria (hepatic) Hepatic disease (e.g., chronic hepatitis, Elevated liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia (plasma
cirrhosis, hepatotoxicity, hepatic neoplasia, yellow) with normal hematocrit
hepatic lipidosis)
Bilirubinuria (posthepatic) Cholestatic disease (cholangiohepatitis, Elevated liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia (plasma
gallbladder mucocele), biliary rupture yellow) with normal hematocrit, ultrasound
imaging of biliary tree
Drugs or dyes Phenazopyridine, fluorescein, nitrofurantoin, History
others
Cloudy, variable Pyuria UTI, sterile cystitis, pyometra WBC on sediment
opaque
Lipiduria Hepatic lipidosis (cats), hyperlipidemia of Lipid droplets on urinalysis, ± hyperlipidemia
any cause, healthy pets
Crystalluria Related to UTI, idiopathic, artifact Crystals on sediment
Pink/red Renal, ureteral disease Primary renal hematuria, glomerulonephritis, RBC on sediment, imaging findings, cystoscopy
renal telangiectasia, renal neoplasia
Bladder, urethral disease UTI, sterile hemorrhagic cystitis, urolithiasis, RBC on sediment, imaging findings
urethritis, feline idiopathic cystitis,
transitional cell carcinoma
Reproductive disease/condition Prostatitis, prostatic neoplasia, estrus RBC on sediment, imaging findings, free catch vs.
cystocentesis or catheter sample (not discolored)
Coagulopathy Thrombocytopenia, DIC, vitamin K RBC on sediment, evidence of bleeding elsewhere,
antagonism thrombocytopenia, increased BMBT, or prolonged
PT/aPTT
Hemoglobin Intravascular hemolysis of any cause, RBC absent on UA, hemoglobinemia (pink plasma)
synthetic hemoglobin administration
Drugs or dyes Phenazopyridine, phenolsulfonphthalein, History
beets, rhubarb
Trauma Abdominal trauma History and examination, imaging studies
www.ExpertConsult.com