Page 2456 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2456
Disinfectants, Antimicrobial Spectrum 1217
(Continued from previous page)
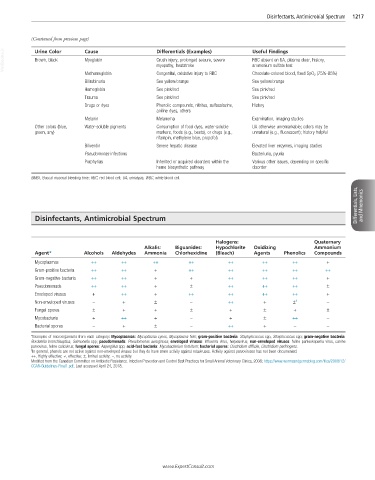
VetBooks.ir Urine Color Cause Differentials (Examples) Useful Findings
Brown, black
RBC absent on UA, plasma clear, history,
Myoglobin
Crush injury, prolonged seizure, severe
myopathy, heatstroke
ammonium sulfate test
Methemoglobin Congenital, oxidative injury to RBC Chocolate-colored blood, fixed SpO 2 (75%-85%)
Bilirubinuria See yellow/orange See yellow/orange
Hemoglobin See pink/red See pink/red
Trauma See pink/red See pink/red
Drugs or dyes Phenolic compounds, nitrites, sulfasalazine, History
aniline dyes, others
Melanin Melanoma Examination, imaging studies
Other colors (blue, Water-soluble pigments Consumption of food dyes, water-soluble UA otherwise unremarkable; colors may be
green, any) markers, foods (e.g., beets), or drugs (e.g., unnatural (e.g., fluorescent); history helpful
rifampin, methylene blue, propofol)
Biliverdin Severe hepatic disease Elevated liver enzymes, imaging studies
Pseudomonas infections Bacteriuria, pyuria
Porphyrias Inherited or acquired disorders within the Various other issues, depending on specific
heme biosynthetic pathway disorder
BMBT, Buccal mucosal bleeding time; RBC, red blood cell; UA, urinalysis; WBC, white blood cell.
Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Disinfectants, Antimicrobial Spectrum
Halogens: Quaternary
Alkalis: Biguanides: Hypochlorite Oxidizing Ammonium
Agent* Alcohols Aldehydes Ammonia Chlorhexidine (Bleach) Agents Phenolics Compounds
Mycoplasmas ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ +
Gram-positive bacteria ++ ++ + ++ ++ ++ ++ ++
Gram-negative bacteria ++ ++ + + ++ ++ ++ +
Pseudomonads ++ ++ + ± ++ ++ ++ ±
Enveloped viruses + ++ + ++ ++ ++ ++ +
Non-enveloped viruses – + ± – ++ + ± † –
Fungal spores ± + + ± + ± + ±
Mycobacteria + ++ + – + ± ++ –
Bacterial spores – + ± – ++ + – –
*Examples of microorganisms from each category: Mycoplasmas: Mycoplasma cynos, Mycoplasma felis; gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp, Streptococcus spp; gram-negative bacteria:
Bordetella bronchiseptica, Salmonella spp; pseudomonads: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; enveloped viruses: influenza virus, herpesvirus; non-enveloped viruses: feline panleukopenia virus, canine
parvovirus, feline calicivirus; fungal spores: Aspergillus spp; acid-fast bacteria: Mycobacterium fortuitum; bacterial spores: Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens.
† In general, phenols are not active against non-enveloped viruses but they do have some activity against rotaviruses. Activity against parvoviruses has not been documented.
++, Highly effective; +, effective; ±, limited activity; –, no activity.
Modified from the Canadian Committee on Antibiotic Resistance. Infection Prevention and Control Best Practices for Small Animal Veterinary Clinics, 2008; https://www.wormsandgermsblog.com/files/2008/12/
CCAR-Guidelines-Final1.pdf. Last accessed April 24, 2018.
www.ExpertConsult.com