Page 2458 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2458
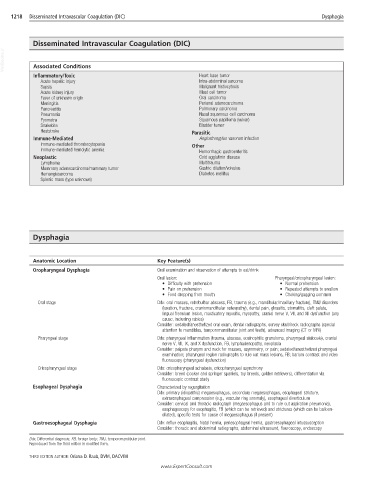
1218 Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Dysphagia
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
VetBooks.ir Associated Conditions
Inflammatory/Toxic Heart base tumor
Acute hepatic injury Intra-abdominal sarcoma
Sepsis Malignant histiocytosis
Acute kidney injury Mast cell tumor
Fever of unknown origin Oral carcinoma
Meningitis Perianal adenocarcinoma
Pancreatitis Pulmonary carcinoma
Pneumonia Nasal squamous cell carcinoma
Pyometra Squamous papilloma (vulvar)
Snakebite Bladder tumor
Heatstroke Parasitic
Immune-Mediated Angiostrongylus vasorum infection
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia Other
Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis
Neoplastic Cold agglutinin disease
Lymphoma Multitrauma
Mammary adenocarcinoma/mammary tumor Gastric dilation/volvulus
Hemangiosarcoma Diabetes mellitus
Splenic mass (type unknown)
Dysphagia
Anatomic Location Key Feature(s)
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Oral examination and observation of attempts to eat/drink
Oral lesion: Pharyngeal/cricopharyngeal lesion:
• Difficulty with prehension • Normal prehension
• Pain on prehension • Repeated attempts to swallow
• Food dropping from mouth • Choking/gagging common
Oral stage Ddx: oral masses, retrobulbar abscess, FB, trauma (e.g., mandibular/maxillary fracture), TMJ disorders
(luxation, fracture, craniomandibular osteopathy), dental pain, glossitis, stomatitis, cleft palate,
lingual frenulum lesion, masticatory myositis, myopathy, cranial nerve V, VII, and XII dysfunction (any
cause, including rabies)
Consider: sedated/anesthetized oral exam, dental radiographs, survey skull/neck radiographs (special
attention to mandibles, temporomandibular joint and teeth), advanced imaging (CT or MRI)
Pharyngeal stage Ddx: pharyngeal inflammation (trauma, abscess, eosinophilic granuloma, pharyngeal sialocele), cranial
nerve V, VII, IX, and X dysfunction, FB, lymphadenopathy, neoplasia
Consider: palpate pharynx and neck for masses, asymmetry, or pain; sedated/anesthetized pharyngeal
examination; pharyngeal region radiographs to rule out mass lesions, FB; barium contrast and video
fluoroscopy (pharyngeal dysfunction)
Cricopharyngeal stage Ddx: cricopharyngeal achalasia, cricopharyngeal asynchrony
Consider: breed (cocker and springer spaniels, toy breeds, golden retrievers), differentiation via
fluoroscopic contrast study
Esophageal Dysphagia Characterized by regurgitation
Ddx: primary (idiopathic) megaesophagus, secondary megaesophagus, esophageal stricture,
extraesophageal compression (e.g., vascular ring anomaly), esophageal diverticulum
Consider: cervical and thoracic radiograph (megaesophagus and to rule out aspiration pneumonia),
esophagoscopy for esophagitis, FB (which can be retrieved) and strictures (which can be balloon-
dilated), specific tests for cause of megaesophagus (if present)
Gastroesophageal Dysphagia Ddx: reflux esophagitis, hiatal hernia, periesophageal hernia, gastroesophageal intussusception
Consider: thoracic and abdominal radiographs, abdominal ultrasound, flouroscopy, endoscopy
Ddx, Differential diagnosis; FB, foreign body; TMJ, temporomandibular joint.
Reproduced from the third edition in modified form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Oriana D. Raab, DVM, DACVIM
www.ExpertConsult.com