Page 2482 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2482
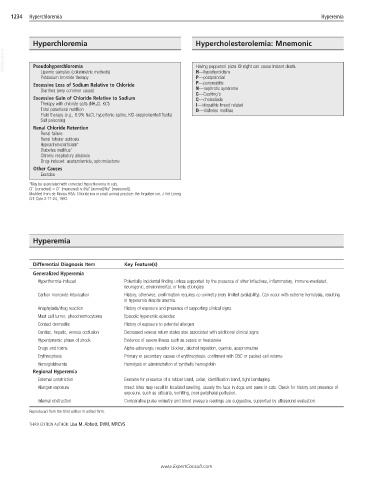
1234 Hyperchloremia Hyperemia
Hyperchloremia Hypercholesterolemia: Mnemonic
VetBooks.ir Pseudohyperchloremia Having pepperoni pizza @ night can cause instant death.
Lipemic samples (colorimetric methods)
Potassium bromide therapy H—hypothyroidism
P—postprandial
Excessive Loss of Sodium Relative to Chloride P—pancreatitis
Diarrhea (very common cause) N—nephrotic syndrome
C—Cushing’s
Excessive Gain of Chloride Relative to Sodium C—cholestasis
Therapy with chloride salts (NH 4 Cl, KCl) I—idiopathic breed related
Total parenteral nutrition D—diabetes mellitus
Fluid therapy (e.g., 0.9% NaCl, hypertonic saline, KCl-supplemented fluids)
Salt poisoning
Renal Chloride Retention
Renal failure
Renal tubular acidosis
Hypoadrenocorticism*
Diabetes mellitus*
Chronic respiratory alkalosis
Drug-induced: acetazolamide, spironolactone
Other Causes
Exercise
*May be associated with corrected hypochloremia in cats.
−
+
+
−
Cl (corrected) = Cl (measured) × (Na [normal]/Na [measured]).
Modified from de Morais HSA: Chloride ion in small animal practice: the forgotten ion. J Vet Emerg
Crit Care 2:11-24, 1992.
Hyperemia
Differential Diagnosis Item Key Feature(s)
Generalized Hyperemia
Hyperthermia-induced Potentially incidental finding unless supported by the presence of other infectious, inflammatory, immune-mediated,
neurogenic, environmental, or toxic etiologies
Carbon monoxide intoxication History; otherwise, confirmation requires co-oximetry (very limited availability). Can occur with extreme hemolysis, resulting
in hyperemia despite anemia.
Anaphylaxis/drug reaction History of exposure and presence of supporting clinical signs
Mast cell tumor, pheochromocytoma Episodic hyperemic episodes
Contact dermatitis History of exposure to potential allergen
Cardiac, hepatic, venous occlusion Decreased venous return states also associated with additional clinical signs
Hyperdynamic phase of shock Evidence of severe illness such as sepsis or heatstroke
Drugs and toxins Alpha-adrenergic receptor blocker, alcohol ingestion, cyanide, acepromazine
Erythrocytosis Primary or secondary causes of erythrocytosis; confirmed with CBC or packed cell volume
Hemoglobinemia Hemolysis or administration of synthetic hemoglobin
Regional Hyperemia
External constriction Examine for presence of a rubber band, collar, identification band, tight bandaging.
Allergen exposure Insect bites may result in localized swelling, usually the face in dogs and paws in cats. Check for history and presence of
exposure, such as urticaria, vomiting, poor peripheral perfusion.
Internal obstruction Comparative pulse oximetry and blood pressure readings are suggestive, supported by ultrasound evaluation.
Reproduced from the third edition in edited form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Lisa M. Abbott, DVM, MRCVS
www.ExpertConsult.com