Page 2480 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2480
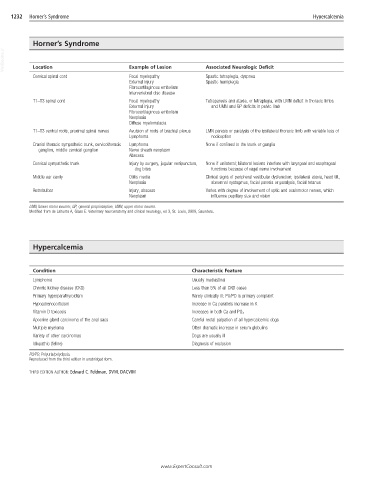
1232 Horner’s Syndrome Hypercalcemia
Horner’s Syndrome
VetBooks.ir Location Example of Lesion Associated Neurologic Deficit
Cervical spinal cord Focal myelopathy Spastic tetraplegia, dyspnea
External injury Spastic hemiplegia
Fibrocartilaginous embolism
Intervertebral disc disease
T1–T3 spinal cord Focal myelopathy Tetraparesis and ataxia, or tetraplegia, with LMN deficit in thoracic limbs
External injury and UMN and GP deficits in pelvic limb
Fibrocartilaginous embolism
Neoplasia
Diffuse myelomalacia
T1–T3 ventral roots, proximal spinal nerves Avulsion of roots of brachial plexus LMN paresis or paralysis of the ipsilateral thoracic limb with variable loss of
Lymphoma nociception
Cranial thoracic sympathetic trunk, cervicothoracic Lymphoma None if confined to the trunk or ganglia
ganglion, middle cervical ganglion Nerve sheath neoplasm
Abscess
Cervical sympathetic trunk Injury by surgery, jugular venipuncture, None if unilateral; bilateral lesions interfere with laryngeal and esophageal
dog bites functions because of vagal nerve involvement
Middle ear cavity Otitis media Clinical signs of peripheral vestibular dysfunction; ipsilateral ataxia, head tilt,
Neoplasia abnormal nystagmus, facial paresis or paralysis, facial tetanus
Retrobulbar Injury, abscess Varies with degree of involvement of optic and oculomotor nerves, which
Neoplasm influence pupillary size and vision
LMN, Lower motor neuron; GP, general proprioceptive; UMN, upper motor neuron.
Modified from de Lahunta A, Glass E: Veterinary neuroanatomy and clinical neurology, ed 3, St. Louis, 2009, Saunders.
Hypercalcemia
Condition Characteristic Feature
Lymphoma Usually mediastinal
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) Less than 5% of all CKD cases
Primary hyperparathyroidism Rarely clinically ill; PU/PD is primary complaint
Hypoadrenocorticism Increase in Ca parallels increase in K
Vitamin D toxicosis Increases in both Ca and PO 4
Apocrine gland carcinoma of the anal sacs Careful rectal palpation of all hypercalcemic dogs
Multiple myeloma Often dramatic increase in serum globulins
Variety of other carcinomas Dogs are usually ill
Idiopathic (feline) Diagnosis of exclusion
PU/PD, Polyuria/polydipsia.
Reproduced from the third edition in unabridged form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Edward C. Feldman, DVM, DACVIM
www.ExpertConsult.com