Page 643 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 643
Lameness of the Proximal Limb 609
VetBooks.ir
B
A
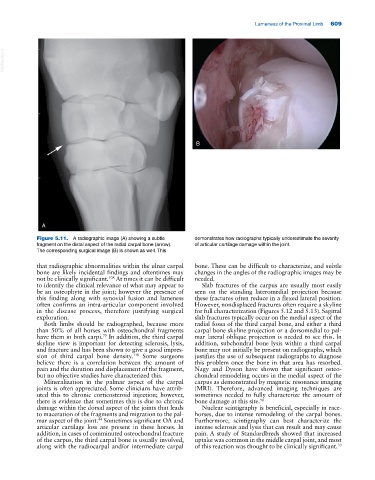
Figure 5.11. A radiographic image (A) showing a subtle demonstrates how radiographs typically underestimate the severity
fragment on the distal aspect of the radial carpal bone (arrow). of articular cartilage damage within the joint.
The corresponding surgical image (B) is shown as well. This
that radiographic abnormalities within the ulnar carpal bone. These can be difficult to characterize, and subtle
bone are likely incidental findings and oftentimes may changes in the angles of the radiographic images may be
not be clinically significant. At times it can be difficult needed.
108
to identify the clinical relevance of what may appear to Slab fractures of the carpus are usually most easily
be an osteophyte in the joint; however the presence of seen on the standing lateromedial projection because
this finding along with synovial fusion and lameness these fractures often reduce in a flexed lateral position.
often confirms an intra‐articular component involved However, nondisplaced fractures often require a skyline
in the disease process, therefore justifying surgical for full characterization (Figures 5.12 and 5.13). Sagittal
exploration. slab fractures typically occur on the medial aspect of the
Both limbs should be radiographed, because more radial fossa of the third carpal bone, and either a third
than 50% of all horses with osteochondral fragments carpal bone skyline projection or a dorsomedial to pal-
79
have them in both carpi. In addition, the third carpal mar lateral oblique projection is needed to see this. In
skyline view is important for detecting sclerosis, lysis, addition, subchondral bone lysis within a third carpal
and fracture and has been shown to give a good impres- bone may not initially be present on radiographs, which
sion of third carpal bone density. Some surgeons justifies the use of subsequent radiographs to diagnose
118
believe there is a correlation between the amount of this problem once the bone in that area has resorbed.
pain and the duration and displacement of the fragment, Nagy and Dyson have shown that significant osteo-
but no objective studies have characterized this. chondral remodeling occurs in the medial aspect of the
Mineralization in the palmar aspect of the carpal carpus as demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging
joints is often appreciated. Some clinicians have attrib- (MRI). Therefore, advanced imaging techniques are
uted this to chronic corticosteroid injection; however, sometimes needed to fully characterize the amount of
there is evidence that sometimes this is due to chronic bone damage at this site. 90
damage within the dorsal aspect of the joints that leads Nuclear scintigraphy is beneficial, especially in race-
to maceration of the fragments and migration to the pal- horses, due to intense remodeling of the carpal bones.
mar aspect of the joint. Sometimes significant OA and Furthermore, scintigraphy can best characterize the
44
articular cartilage loss are present in these horses. In intense sclerosis and lysis that can result and may cause
addition, in cases of comminuted osteochondral fracture pain. A study of Standardbreds showed that increased
of the carpus, the third carpal bone is usually involved, uptake was common in the middle carpal joint, and most
along with the radiocarpal and/or intermediate carpal of this reaction was thought to be clinically significant.
33