Page 832 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 832
798 Chapter 6
VetBooks.ir
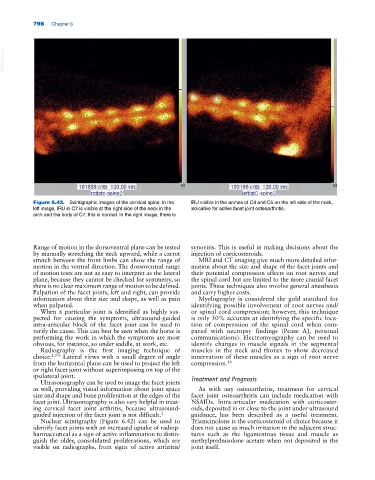
Figure 6.42. Scintigraphic images of the cervical spine. In the IRU visible in the arches of C4 and C5 on the left side of the neck,
left image, IRU in C7 is visible at the right side of the neck in the indicative for active facet joint osteoarthritis.
arch and the body of C7; this is normal. In the right image, there is
Range of motion in the dorsoventral plane can be tested synovitis. This is useful in making decisions about the
by manually stretching the neck upward, while a carrot injection of corticosteroids.
stretch between the front limbs can show the range of MRI and CT imaging give much more detailed infor-
motion in the ventral direction. The dorsoventral range mation about the size and shape of the facet joints and
of motion tests are not as easy to interpret as the lateral their potential compression effects on root nerves and
plane, because they cannot be checked for symmetry, so the spinal cord but are limited to the more cranial facet
there is no clear maximum range of motion to be defined. joints. These techniques also involve general anesthesia
Palpation of the facet joints, left and right, can provide and carry higher costs.
information about their size and shape, as well as pain Myelography is considered the gold standard for
when palpated. identifying possible involvement of root nerves and/
When a particular joint is identified as highly sus- or spinal cord compression; however, this technique
pected for causing the symptoms, ultrasound‐guided is only 50% accurate at identifying the specific loca-
intra‐articular block of the facet joint can be used to tion of compression of the spinal cord when com-
verify the cause. This can best be seen when the horse is pared with necropsy findings (Pease AJ, personal
performing the work in which the symptoms are most communications). Electromyography can be used to
obvious, for instance, so under saddle, at work, etc. identify changes in muscle signals in the segmental
Radiography is the first imaging technique of muscles in the neck and thorax to show decreased
choice. 1,7–9 Lateral views with a small degree of angle innervation of these muscles as a sign of root nerve
from the horizontal plane can be used to project the left compression. 16
or right facet joint without superimposing on top of the
ipsilateral joint. Treatment and Prognosis
Ultrasonography can be used to image the facet joints
as well, providing visual information about joint space As with any osteoarthritis, treatment for cervical
size and shape and bone proliferation at the edges of the facet joint osteoarthritis can include medication with
facet joint. Ultrasonography is also very helpful in treat- NSAIDs. Intra‐articular medication with corticoster-
ing cervical facet joint arthritis, because ultrasound‐ oids, deposited in or close to the joint under ultrasound
guided injection of the facet joint is not difficult. 2 guidance, has been described as a useful treatment.
Nuclear scintigraphy (Figure 6.42) can be used to Triamcinolone is the corticosteroid of choice because it
identify facet joints with an increased uptake of radiop- does not cause as much irritation in the adjacent struc-
harmaceutical as a sign of active inflammation to distin- tures such as the ligamentous tissue and muscle as
guish the older, consolidated proliferations, which are methylprednisolone acetate when not deposited in the
visible on radiographs, from signs of active arthritis/ joint itself.