Page 261 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 261
246 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
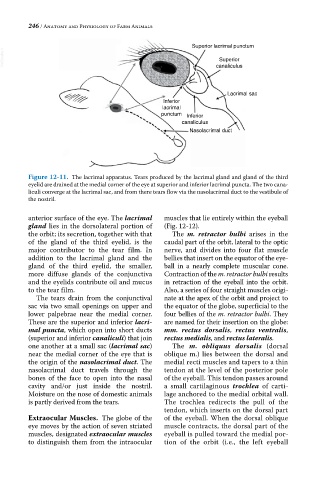
Superior lacrimal punctum
VetBooks.ir canaliculus
Superior
Lacrimal sac
Inferior
lacrimal
punctum Inferior
canaliculus
Nasolacrimal duct
Figure 12-11. The lacrimal apparatus. Tears produced by the lacrimal gland and gland of the third
eyelid are drained at the medial corner of the eye at superior and inferior lacrimal puncta. The two cana
liculi converge at the lacrimal sac, and from there tears flow via the nasolacrimal duct to the vestibule of
the nostril.
anterior surface of the eye. The lacrimal muscles that lie entirely within the eyeball
gland lies in the dorsolateral portion of (Fig. 12‐12).
the orbit; its secretion, together with that The m. retractor bulbi arises in the
of the gland of the third eyelid, is the caudal part of the orbit, lateral to the optic
major contributor to the tear film. In nerve, and divides into four flat muscle
addition to the lacrimal gland and the bellies that insert on the equator of the eye
gland of the third eyelid, the smaller, ball in a nearly complete muscular cone.
more diffuse glands of the conjunctiva Contraction of the m. retractor bulbi results
and the eyelids contribute oil and mucus in retraction of the eyeball into the orbit.
to the tear film. Also, a series of four straight muscles origi
The tears drain from the conjunctival nate at the apex of the orbit and project to
sac via two small openings on upper and the equator of the globe, superficial to the
lower palpebrae near the medial corner. four bellies of the m. retractor bulbi. They
These are the superior and inferior lacri are named for their insertion on the globe:
mal puncta, which open into short ducts mm. rectus dorsalis, rectus ventralis,
(superior and inferior canaliculi) that join rectus medialis, and rectus lateralis.
one another at a small sac (lacrimal sac) The m. obliquus dorsalis (dorsal
near the medial corner of the eye that is oblique m.) lies between the dorsal and
the origin of the nasolacrimal duct. The medial recti muscles and tapers to a thin
nasolacrimal duct travels through the tendon at the level of the posterior pole
bones of the face to open into the nasal of the eyeball. This tendon passes around
cavity and/or just inside the nostril. a small cartilaginous trochlea of carti
Moisture on the nose of domestic animals lage anchored to the medial orbital wall.
is partly derived from the tears. The trochlea redirects the pull of the
tendon, which inserts on the dorsal part
Extraocular Muscles. The globe of the of the eyeball. When the dorsal oblique
eye moves by the action of seven striated muscle contracts, the dorsal part of the
muscles, designated extraocular muscles eyeball is pulled toward the medial por
to distinguish them from the intraocular tion of the orbit (i.e., the left eyeball