Page 263 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 263
248 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
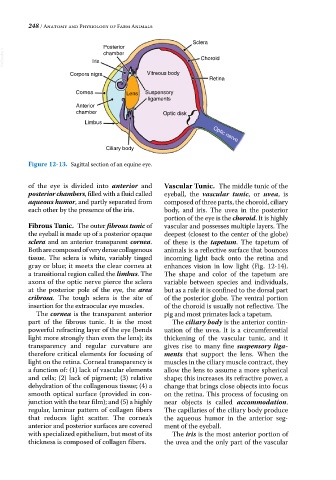
Sclera
Posterior
VetBooks.ir Iris chamber Choroid
Corpora nigra Vitreous body
Retina
Cornea Lens Suspensory
ligaments
Anterior
chamber Optic disk
Limbus Optic nerve
Ciliary body
Figure 12-13. Sagittal section of an equine eye.
of the eye is divided into anterior and Vascular Tunic. The middle tunic of the
posterior chambers, filled with a fluid called eyeball, the vascular tunic, or uvea, is
aqueous humor, and partly separated from composed of three parts, the choroid, ciliary
each other by the presence of the iris. body, and iris. The uvea in the posterior
portion of the eye is the choroid. It is highly
Fibrous Tunic. The outer fibrous tunic of vascular and possesses multiple layers. The
the eyeball is made up of a posterior opaque deepest (closest to the center of the globe)
sclera and an anterior transparent cornea. of these is the tapetum. The tapetum of
Both are composed of very dense collagenous animals is a reflective surface that bounces
tissue. The sclera is white, variably tinged incoming light back onto the retina and
gray or blue; it meets the clear cornea at enhances vision in low light (Fig. 12‐14).
a transitional region called the limbus. The The shape and color of the tapetum are
axons of the optic nerve pierce the sclera variable between species and individuals,
at the posterior pole of the eye, the area but as a rule it is confined to the dorsal part
cribrosa. The tough sclera is the site of of the posterior globe. The ventral portion
insertion for the extraocular eye muscles. of the choroid is usually not reflective. The
The cornea is the transparent anterior pig and most primates lack a tapetum.
part of the fibrous tunic. It is the most The ciliary body is the anterior contin
powerful refracting layer of the eye (bends uation of the uvea. It is a circumferential
light more strongly than even the lens); its thickening of the vascular tunic, and it
transparency and regular curvature are gives rise to many fine suspensory liga
therefore critical elements for focusing of ments that support the lens. When the
light on the retina. Corneal transparency is muscles in the ciliary muscle contract, they
a function of: (1) lack of vascular elements allow the lens to assume a more spherical
and cells; (2) lack of pigment; (3) relative shape; this increases its refractive power, a
dehydration of the collagenous tissue; (4) a change that brings close objects into focus
smooth optical surface (provided in con on the retina. This process of focusing on
junction with the tear film); and (5) a highly near objects is called accommodation.
regular, laminar pattern of collagen fibers The capillaries of the ciliary body produce
that reduces light scatter. The cornea’s the aqueous humor in the anterior seg
anterior and posterior surfaces are covered ment of the eyeball.
with specialized epithelium, but most of its The iris is the most anterior portion of
thickness is composed of collagen fibers. the uvea and the only part of the vascular