Page 262 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 262
Sense Organs / 247
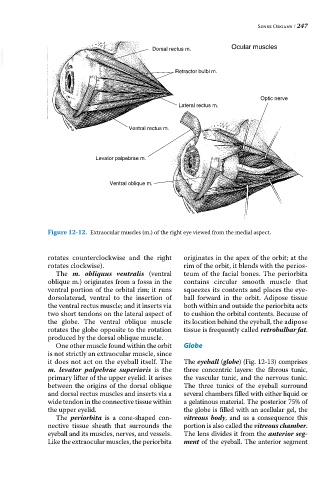
VetBooks.ir Dorsal rectus m. Ocular muscles
Retractor bulbi m.
Optic nerve
Lateral rectus m.
Ventral rectus m.
Levator palpebrae m.
Ventral oblique m.
Figure 12-12. Extraocular muscles (m.) of the right eye viewed from the medial aspect.
rotates counterclockwise and the right originates in the apex of the orbit; at the
rotates clockwise). rim of the orbit, it blends with the perios
The m. obliquus ventralis (ventral teum of the facial bones. The periorbita
oblique m.) originates from a fossa in the contains circular smooth muscle that
ventral portion of the orbital rim; it runs squeezes its contents and places the eye
dorsolaterad, ventral to the insertion of ball forward in the orbit. Adipose tissue
the ventral rectus muscle; and it inserts via both within and outside the periorbita acts
two short tendons on the lateral aspect of to cushion the orbital contents. Because of
the globe. The ventral oblique muscle its location behind the eyeball, the adipose
rotates the globe opposite to the rotation tissue is frequently called retrobulbar fat.
produced by the dorsal oblique muscle.
One other muscle found within the orbit Globe
is not strictly an extraocular muscle, since
it does not act on the eyeball itself. The The eyeball (globe) (Fig. 12‐13) comprises
m. levator palpebrae superioris is the three concentric layers: the fibrous tunic,
primary lifter of the upper eyelid. It arises the vascular tunic, and the nervous tunic.
between the origins of the dorsal oblique The three tunics of the eyeball surround
and dorsal rectus muscles and inserts via a several chambers filled with either liquid or
wide tendon in the connective tissue within a gelatinous material. The posterior 75% of
the upper eyelid. the globe is filled with an acellular gel, the
The periorbita is a cone‐shaped con vitreous body, and as a consequence this
nective tissue sheath that surrounds the portion is also called the vitreous chamber.
eyeball and its muscles, nerves, and vessels. The lens divides it from the anterior seg
Like the extraocular muscles, the periorbita ment of the eyeball. The anterior segment