Page 205 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 205
17 Electrocardiography 173
Table 17.4 ECG criteria for heart enlargement in the dog and cat
VetBooks.ir Dog Cat
Left atrial enlargement
I I P‐wave >0.4 mV, >0.04 s >0.04 s
Notched
Right atrial enlargement
P‐wave >0.4 mV >0.2 mV
Left ventricular enlargement
R‐wave >2.5 mV in lead >0.9 mV in
I I I II, aVF lead II
>3.0 mV in
large‐breed dogs
>1.5 mV in lead I
QRS duration* >0.06 s >0.04 s
Right ventricular enlargement
aVR
S‐wave >0.35 mV in S‐wave in
lead II leads I, II,
>0.05 mV in III and aVF
lead I (>0.5 mV)
S‐wave in leads
I, II III and aVF
aVL
Electrical axis Right shift Right shift
(>+100°) (>+160°)
Source: Adapted from Tilley and Smith 2008.
* QRS duration >0.08 s in the dog and >0.06 s in the cat can be associated
with left or right bundle branch blocks. See text for more detail.
aVF
recording. RBBB (see Figure 17.10) is characterized by
a right shift of the MEA and markedly prolonged QRS
duration (>0.08 s in the dog and >0.06 s in the cat),
while LBBB (Figure 17.12) is characterized by a normal
MEA and markedly prolonged QRS duration (>0.08 s
in the dog and >0.06 s in the cat) (normal values listed
in Table 17.3).
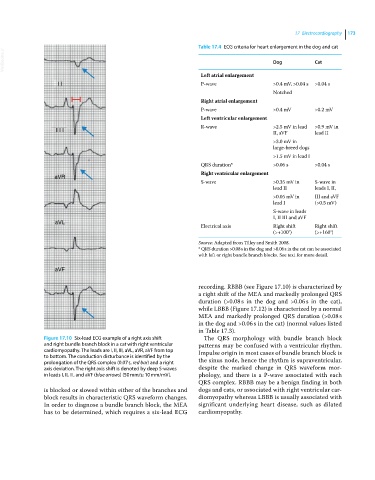
Figure 17.10 Six‐lead ECG example of a right axis shift The QRS morphology with bundle branch block
and right bundle branch block in a cat with right ventricular patterns may be confused with a ventricular rhythm.
cardiomyopathy. The leads are I, II, III, aVL, aVR, aVF from top Impulse origin in most cases of bundle branch block is
to bottom. The conduction disturbance is identified by the
prolongation of the QRS complex (0.07 s, red bar) and a right the sinus node, hence the rhythm is supraventricular,
axis deviation. The right axis shift is denoted by deep S‐waves despite the marked change in QRS waveform mor-
in leads I, II, III, and aVF (blue arrows) (50 mm/s; 10 mm/mV). phology, and there is a P‐wave associated with each
QRS complex. RBBB may be a benign finding in both
is blocked or slowed within either of the branches and dogs and cats, or associated with right ventricular car-
block results in characteristic QRS waveform changes. diomyopathy whereas LBBB is usually associated with
In order to diagnose a bundle branch block, the MEA significant underlying heart disease, such as dilated
has to be determined, which requires a six‐lead ECG cardiomyopathy.