Page 1241 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 1241
Appendices 1293
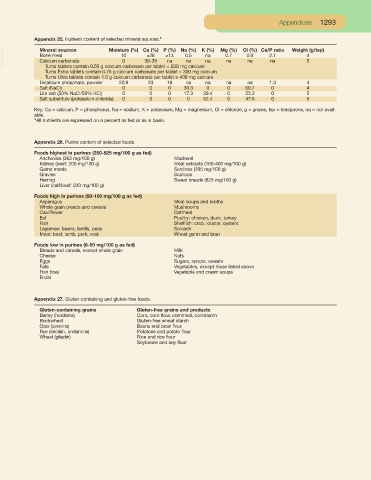
Appendix 25. Nutrient content of selected mineral sources.*
VetBooks.ir Mineral sources Moisture (%) Ca (%) P (%) Na (%) K (%) Mg (%) Cl (%) Ca/P ratio Weight (g/tsp)
Bone meal
0.5
≥13
≥28
10
2.1
0.7
0.0
4
na
na
na
na
na
0
36-39
na
5
Calcium carbonate
na
Tums tablets contain 0.50 g calcium carbonate per tablet = 200 mg calcium
Tums Extra tablets contain 0.75 g calcium carbonate per tablet = 300 mg calcium
Tums Ultra tablets contain 1.0 g calcium carbonate per tablet = 400 mg calcium
Dicalcium phosphate, powder 20.9 23 18 na na na na 1.3 4
Salt (NaCl) 0 0 0 39.3 0 0 60.7 0 4
Lite salt (50% NaCl/50% KCl) 0 0 0 17.3 29.4 0 53.3 0 5
Salt substitute (potassium chloride) 0 0 0 0 52.4 0 47.6 0 5
Key: Ca = calcium, P = phosphorus, Na = sodium, K = potassium, Mg = magnesium, Cl = chloride, g = grams, tsp = teaspoons, na = not avail-
able.
*All nutrients are expressed on a percent as fed or as is basis.
Appendix 26. Purine content of selected foods.
Foods highest in purines (250-825 mg/100 g as fed)
Anchovies (363 mg/100 g) Mackerel
Kidney (beef: 200 mg/100 g) Meat extracts (160-400 mg/100 g)
Game meats Sardines (295 mg/100 g)
Gravies Scallops
Herring Sweat breads (825 mg/100 g)
Liver (calf/beef: 233 mg/100 g)
Foods high in purines (50-150 mg/100 g as fed)
Asparagus Meat soups and broths
Whole grain breads and cereals Mushrooms
Cauliflower Oatmeal
Eel Poultry: chicken, duck, turkey
Fish Shellfish: crab, lobster, oysters
Legumes: beans, lentils, peas Spinach
Meat: beef, lamb, pork, veal Wheat germ and bran
Foods low in purines (0-50 mg/100 g as fed)
Breads and cereals, except whole grain Milk
Cheese Nuts
Eggs Sugars, syrups, sweets
Fats Vegetables, except those listed above
Fish (roe) Vegetable and cream soups
Fruits
Appendix 27. Gluten-containing and gluten-free foods.
Gluten-containing grains Gluten-free grains and products
Barley (hordeins) Corn, corn flour, cornmeal, cornstarch
Buckwheat Gluten-free wheat starch
Oats (avenins) Beans and bean flour
Rye (secalin, prolamins) Potatoes and potato flour
Wheat (gliadin) Rice and rice flour
Soybeans and soy flour