Page 261 - Six Sigma Advanced Tools for Black Belts and Master Black Belts
P. 261
OTE/SPH
OTE/SPH
3:5
Char Count= 0
August 31, 2006
JWBK119-16
246 A Glossary for Design of Experiments with Examples
1,200
1024
1,000
Runs per Replicate 800 512
600
400
200 64 128 256
2 4 8 16 32
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Number of Factors, k
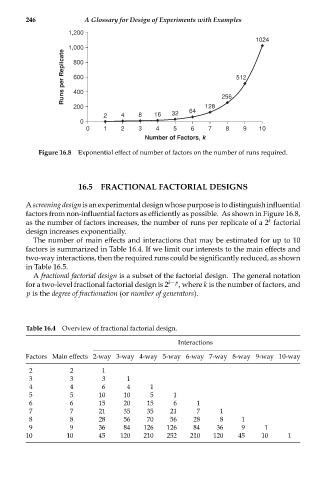
Figure 16.8 Exponential effect of number of factors on the number of runs required.
16.5 FRACTIONAL FACTORIAL DESIGNS
Ascreeningdesignisanexperimentaldesignwhosepurposeistodistinguishinfluential
factors from non-influential factors as efficiently as possible. As shown in Figure 16.8,
k
as the number of factors increases, the number of runs per replicate of a 2 factorial
design increases exponentially.
The number of main effects and interactions that may be estimated for up to 10
factors is summarized in Table 16.4. If we limit our interests to the main effects and
two-way interactions, then the required runs could be significantly reduced, as shown
in Table 16.5.
A fractional factorial design is a subset of the factorial design. The general notation
for a two-level fractional factorial design is 2 k−p , where k is the number of factors, and
p is the degree of fractionation (or number of generators).
Table 16.4 Overview of fractional factorial design.
Interactions
Factors Main effects 2-way 3-way 4-way 5-way 6-way 7-way 8-way 9-way 10-way
2 2 1
3 3 3 1
4 4 6 4 1
5 5 10 10 5 1
6 6 15 20 15 6 1
7 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
8 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1
9 9 36 84 126 126 84 36 9 1
10 10 45 120 210 252 210 120 45 10 1