Page 116 - Essential Haematology
P. 116
102 / Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin
(a) (b)
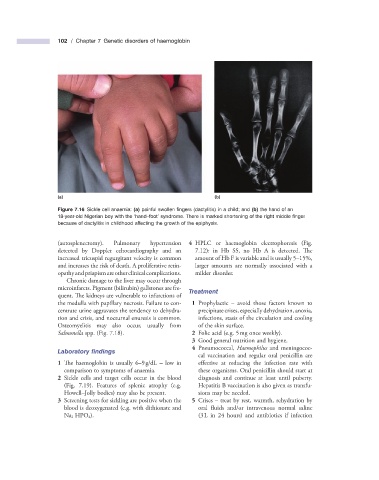
Figure 7.16 Sickle cell anaemia: (a) painful swollen fi ngers (dactylitis) in a child; and (b) the hand of an
18 - year - old Nigerian boy with the ‘ hand – foot ’ syndrome. There is marked shortening of the right middle fi nger
because of dactylitis in childhood affecting the growth of the epiphysis.
(autosplenectomy). Pulmonary hypertension 4 HPLC or haemoglobin electrophoresis (Fig.
detected by Doppler echocardiography and an 7.12 ): in Hb SS, no Hb A is detected. Th e
increased tricuspid regurgitant velocity is common amount of Hb F is variable and is usually 5 – 15%,
and increases the risk of death. A proliferative retin- larger amounts are normally associated with a
opathy and priapism are other clinical complications. milder disorder.
Chronic damage to the liver may occur through
microinfarcts. Pigment (bilirubin) gallstones are fre- Treatment
quent. The kidneys are vulnerable to infarctions of
the medulla with papillary necrosis. Failure to con- 1 Prophylactic – avoid those factors known to
centrate urine aggravates the tendency to dehydra- precipitate crises, especially dehydration, anoxia,
tion and crisis, and nocturnal enuresis is common. infections, stasis of the circulation and cooling
Osteomyelitis may also occur, usually from of the skin surface.
Salmonella spp. (Fig. 7.18 ). 2 Folic acid (e.g. 5 mg once weekly).
3 Good general nutrition and hygiene.
4 Pneumococcal, Haemophilus and meningococ-
Laboratory fi ndings
cal vaccination and regular oral penicillin are
1 The haemoglobin is usually 6 – 9 g/dL – low in effective at reducing the infection rate with
comparison to symptoms of anaemia. these organisms. Oral penicillin should start at
2 Sickle cells and target cells occur in the blood diagnosis and continue at least until puberty.
(Fig. 7.19 ). Features of splenic atrophy (e.g. Hepatitis B vaccination is also given as transfu-
Howell – Jolly bodies) may also be present. sions may be needed.
3 Screening tests for sickling are positive when the 5 Crises – treat by rest, warmth, rehydration by
blood is deoxygenated (e.g. with dithionate and oral fluids and/or intravenous normal saline
Na 2 HPO 4 ). (3 L in 24 hours) and antibiotics if infection