Page 117 - Essential Haematology
P. 117
Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin / 103
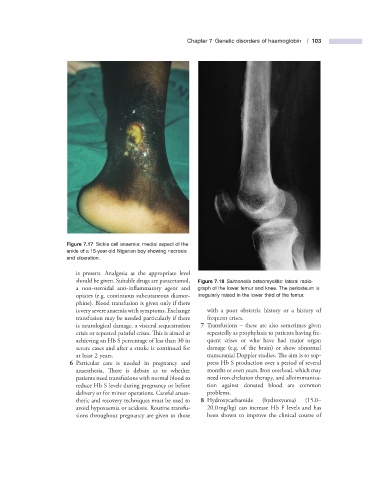
Figure 7.17 Sickle cell anaemia: medial aspect of the
ankle of a 15 - year - old Nigerian boy showing necrosis
and ulceration.
is present. Analgesia at the appropriate level
should be given. Suitable drugs are paracetamol, Figure 7.18 Salmonella osteomyelitis: lateral radio-
a non - steroidal anti - inflammatory agent and graph of the lower femur and knee. The periosteum is
opiates (e.g. continuous subcutaneous diamor- irregularly raised in the lower third of the femur.
phine). Blood transfusion is given only if there
is very severe anaemia with symptoms. Exchange with a poor obstetric history or a history of
transfusion may be needed particularly if there frequent crises.
is neurological damage, a visceral sequestration 7 Transfusions – these are also sometimes given
crisis or repeated painful crises. This is aimed at repeatedly as prophylaxis to patients having fre-
achieving an Hb S percentage of less than 30 in quent crises or who have had major organ
severe cases and after a stroke is continued for damage (e.g. of the brain) or show abnormal
at least 2 years. transcranial Doppler studies. The aim is to sup-
6 Particular care is needed in pregnancy and press Hb S production over a period of several
anaesthesia. There is debate as to whether months or even years. Iron overload, which may
patients need transfusions with normal blood to need iron chelation therapy, and alloimmuniza-
reduce Hb S levels during pregnancy or before tion against donated blood are common
delivery or for minor operations. Careful anaes- problems.
thetic and recovery techniques must be used to 8 Hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea) (15.0 –
avoid hypoxaemia or acidosis. Routine transfu- 20.0 mg/kg) can increase Hb F levels and has
sions throughout pregnancy are given to those been shown to improve the clinical course of