Page 124 - Essential Haematology
P. 124
110 / Chapter 8 White cells: Granulocytes and monocytes
precursor cells and plasma cells, which make up stage and predominate in the mature neutrophil
the immunocyte population, are considered in (Fig 8.7 ). Both types of granule are lysosomal in
Chapter 9 . origin (Fig. 8.7 ). The lifespan of neutrophils in the
The function of phagocytes and immunocytes blood is only 6 – 10 hours.
in protecting the body against infection is closely
connected with two soluble protein systems of the
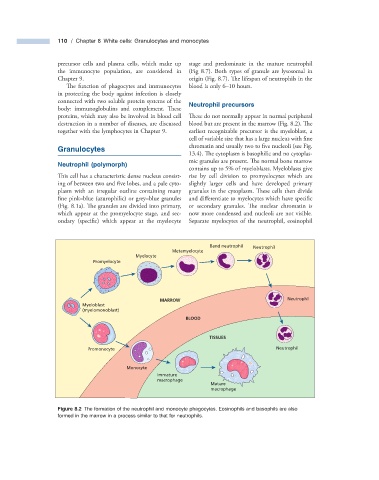
Neutrophil p recursors
body: immunoglobulins and complement. Th ese
proteins, which may also be involved in blood cell These do not normally appear in normal peripheral
destruction in a number of diseases, are discussed blood but are present in the marrow (Fig. 8.2 ). Th e
together with the lymphocytes in Chapter 9 . earliest recognizable precursor is the myeloblast, a
cell of variable size that has a large nucleus with fi ne
chromatin and usually two to five nucleoli (see Fig.
Granulocytes
13.4 ). The cytoplasm is basophilic and no cytoplas-
mic granules are present. The normal bone marrow
Neutrophil ( p olymorph)
contains up to 5% of myeloblasts. Myeloblasts give
This cell has a characteristic dense nucleus consist- rise by cell division to promyelocytes which are
ing of between two and five lobes, and a pale cyto- slightly larger cells and have developed primary
plasm with an irregular outline containing many granules in the cytoplasm. These cells then divide
fine pink – blue (azurophilic) or grey – blue granules and differentiate to myelocytes which have specifi c
(Fig. 8.1 a). The granules are divided into primary, or secondary granules. The nuclear chromatin is
which appear at the promyelocyte stage, and sec- now more condensed and nucleoli are not visible.
ondary (specific) which appear at the myelocyte Separate myelocytes of the neutrophil, eosinophil
Band neutrophil Neutrophil
Metamyelocyte
Myelocyte
Promyelocyte
MARROW Neutrophil
Myeloblast
(myelomonoblast)
BLOOD
TISSUES
Promonocyte Neutrophil
Monocyte
Immature
macrophage
Mature
macrophage
Figure 8.2 The formation of the neutrophil and monocyte phagocytes. Eosinophils and basophils are also
formed in the marrow in a process similar to that for neutrophils.