Page 128 - Essential Haematology
P. 128
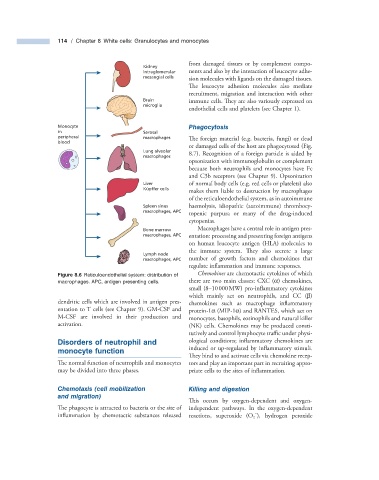
114 / Chapter 8 White cells: Granulocytes and monocytes
from damaged tissues or by complement compo-
Kidney
intraglomerular nents and also by the interaction of leucocyte adhe-
mesangial cells sion molecules with ligands on the damaged tissues.
The leucocyte adhesion molecules also mediate
recruitment, migration and interaction with other
Brain immune cells. They are also variously expressed on
microglia
endothelial cells and platelets (see Chapter 1 ).
Monocyte Phagocytosis
in Serosal
peripheral macrophages The foreign material (e.g. bacteria, fungi) or dead
blood
or damaged cells of the host are phagocytosed (Fig.
Lung alveolar
macrophages 8.7 ). Recognition of a foreign particle is aided by
opsonization with immunoglobulin or complement
because both neutrophils and monocytes have Fc
and C3b receptors (see Chapter 9 ). Opsonization
Liver of normal body cells (e.g. red cells or platelets) also
Küpffer cells
makes them liable to destruction by macrophages
of the reticuloendothelial system, as in autoimmune
Spleen sinus haemolysis, idiopathic (autoimmune) thrombocy-
macrophages, APC
topenic purpura or many of the drug - induced
cytopenias.
Bone marrow Macrophages have a central role in antigen pres-
macrophages, APC entation: processing and presenting foreign antigens
on human leucocyte antigen (HLA) molecules to
the immune system. They also secrete a large
Lymph node
macrophages, APC number of growth factors and chemokines that
regulate inflammation and immune responses.
Figure 8.6 Reticuloendothelial system: distribution of Chemokines are chemotactic cytokines of which
macrophages. APC, antigen presenting cells. there are two main classes: CXC ( α ) chemokines,
small (8 – 10 000 MW) pro - infl ammatory cytokines
which mainly act on neutrophils, and CC ( β )
dendritic cells which are involved in antigen pres- chemokines such as macrophage infl ammatory
entation to T cells (see Chapter 9 ). GM - CSF and protein - 1 α (MIP - 1 α ) and RANTES, which act on
M - CSF are involved in their production and monocytes, basophils, eosinophils and natural killer
activation. (NK) cells. Chemokines may be produced consti-
tutively and control lymphocyte traffi c under physi-
Disorders of n eutrophil and ological conditions; inflammatory chemokines are
m onocyte f unction induced or up - regulated by infl ammatory stimuli.
They bind to and activate cells via chemokine recep-
The normal function of neutrophils and monocytes tors and play an important part in recruiting appro-
may be divided into three phases. priate cells to the sites of infl ammation.
Chemotaxis ( c ell m obilization Killing and d igestion
and m igration)
This occurs by oxygen - dependent and oxygen -
The phagocyte is attracted to bacteria or the site of independent pathways. In the oxygen - dependent
inflammation by chemotactic substances released reactions, superoxide (O 2 ), hydrogen peroxide
−