Page 125 - Essential Haematology
P. 125
Chapter 8 White cells: Granulocytes and monocytes / 111
and basophil series can be indentifi ed. Th e myelo- nuclear lobes (Fig. 8.1 b). Eosinophil myelocytes can
cytes give rise by cell division and diff erentiation to be recognized but earlier stages are indistinguishable
metamyelocytes, non - dividing cells, which have an from neutrophil precursors. The blood transit time
indented or horseshoe - shaped nucleus and a cyto- for eosinophils is longer than for neutrophils. Th ey
plasm filled with primary and secondary granules. enter inflammatory exudates and have a special role
Neutrophil forms between the metamyelocyte and in allergic responses, defence against parasites and
fully mature neutrophil are termed ‘ band ’ , ‘ stab ’ or removal of fibrin formed during infl ammation.
‘ juvenile ’ . These cells may occur in normal periph-
eral blood. They do not contain the clear, fi ne fi la-
Basophils
mentous connections between nuclear lobes that is
seen in mature neutrophils. These are only occasionally seen in normal periph-
eral blood. They have many dark cytoplasmic gran-
ules which overlie the nucleus and contain heparin
Monocytes
and histamine (Fig. 8.1 c). In the tissues they become
These are usually larger than other peripheral blood mast cells. They have immunoglobulin E (IgE)
leucocytes and possess a large central oval or attachment sites and their degranulation is associ-
indented nucleus with clumped chromatin (Fig. ated with histamine release.
8.1 d). The abundant cytoplasm stains blue and con-
tains many fine vacuoles, giving a ground - glass Granulopoiesis
appearance. Cytoplasmic granules are also often
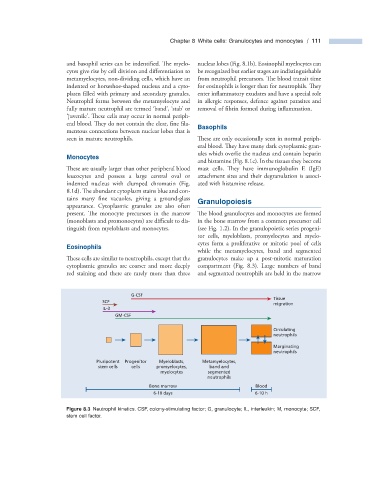
present. The monocyte precursors in the marrow The blood granulocytes and monocytes are formed
(monoblasts and promonocytes) are diffi cult to dis- in the bone marrow from a common precursor cell
tinguish from myeloblasts and monocytes. (see Fig. 1.2 ). In the granulopoietic series progeni-
tor cells, myeloblasts, promyelocytes and myelo-
cytes form a proliferative or mitotic pool of cells
Eosinophils
while the metamyelocytes, band and segmented
These cells are similar to neutrophils, except that the granulocytes make up a post - mitotic maturation
cytoplasmic granules are coarser and more deeply compartment (Fig. 8.3 ). Large numbers of band
red staining and there are rarely more than three and segmented neutrophils are held in the marrow
G-CSF
Tissue
SCF
migration
IL-3
GM-CSF
Circulating
neutrophils
Marginating
neutrophils
Pluripotent Progenitor Myeloblasts, Metamyelocytes,
stem cells cells promyelocytes, band and
myelocytes segmented
neutrophils
Bone marrow Blood
6-10 days 6-10 h
Figure 8.3 Neutrophil kinetics. CSF, colony - stimulating factor; G, granulocyte; IL, interleukin; M, monocyte; SCF,
stem cell factor.