Page 134 - Essential Haematology
P. 134
120 / Chapter 8 White cells: Granulocytes and monocytes
Management occurs within 1 – 2 weeks after stopping the drug.
Patients with chronic neutropenia have recurrent
The treatment of patients with acute severe neutro-
infections which are mainly bacterial in origin
penia is described on p. 169 . In many patients with
although fungal and viral infections (especially
drug - induced neutropenia spontaneous recovery
herpes) also occur. Early recognition and vigorous
treatment with antibiotics, antifungal or antiviral
agents, as appropriate, is essential. Prophylactic
antibacterial agents (e.g. oral co - trimoxazole or cip-
rofloxacin and colistin) and antifungal agents (e.g.
oral amphotericin and fluconazole or itraconazole)
may be of value in reducing the incidence and sever-
ity of infections caused by severe neutropenia. Th e
haemopoietic growth factor G - CSF may be used to
stimulate neutrophil production and is eff ective in
a variety of benign chronic neutropenic states.
Corticosteroid therapy or splenectomy has been
associated with good results in some patients with
autoimmune neutropenia. Rituximab (anti - CD20)
may also be effective. Conversely, corticosteroids
impair neutrophil function and should not be used
indiscriminately in patients with neutropenia.
Monocytosis
9
A rise in blood monocyte count above 0.8 × 10 /L
is infrequent. The conditions listed in Table 8.5 may
be responsible.
Eosinophilic l eucocytosis ( e osinophilia)
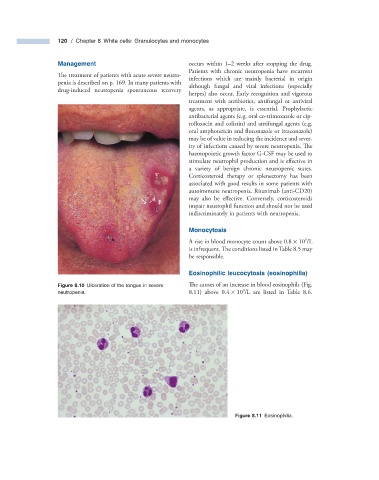
Figure 8.10 Ulceration of the tongue in severe The causes of an increase in blood eosinophils (Fig.
9
neutropenia. 8.11 ) above 0.4 × 10 /L are listed in Table 8.6 .
Figure 8.11 Eosinophilia.