Page 137 - Essential Haematology
P. 137
Chapter 8 White cells: Granulocytes and monocytes / 123
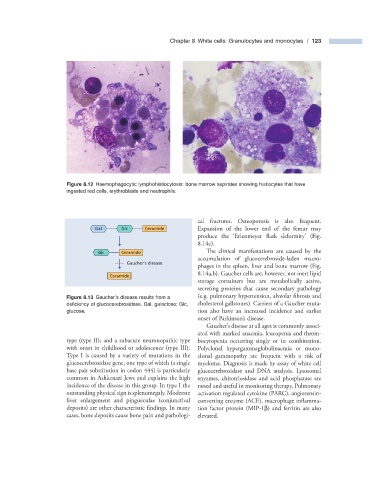
Figure 8.12 Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: bone marrow aspirates showing histiocytes that have
ingested red cells, erythroblasts and neutrophils.
cal fractures. Osteoporosis is also frequent.
Gal Glc Ceramide Expansion of the lower end of the femur may
produce the ‘ Erlenmeyer flask deformity ’ (Fig.
8.14 c).
The clinical manifestations are caused by the
Glc Ceramide
accumulation of glucocerebroside - laden macro-
Gaucher's disease
phages in the spleen, liver and bone marrow (Fig.
8.14 a,b). Gaucher cells are, however, not inert lipid
Ceramide
storage containers but are metabolically active,
secreting proteins that cause secondary pathology
Figure 8.13 Gaucher ’ s disease results from a (e.g. pulmonary hypertension, alveolar fi brosis and
defi ciency of glucocerebrosidase. Gal, galactose; Glc, cholesterol gallstones). Carriers of a Gaucher muta-
glucose. tion also have an increased incidence and earlier
onset of Parkinson ’ s disease.
Gaucher s disease at all ages is commonly associ-
’
ated with marked anaemia, leucopenia and throm-
type (type II); and a subacute neuronopathic type bocytopenia occurring singly or in combination.
with onset in childhood or adolescence (type III). Polyclonal hypergammaglobulinaemia or mono-
Type I is caused by a variety of mutations in the clonal gammopathy are frequent with a risk of
glucocerebrosidase gene, one type of which (a single myeloma. Diagnosis is made by assay of white cell
base pair substitution in codon 444) is particularly glucocerebrosidase and DNA analysis. Lysosomal
common in Ashkenazi Jews and explains the high enyzmes, chitotriosidase and acid phosphatase are
incidence of the disease in this group. In type I the raised and useful in monitoring therapy. Pulmonary
outstanding physical sign is splenomegaly. Moderate activation regulated cytokine (PARC), angiotensin -
liver enlargement and pingueculae (conjunctival converting enzyme (ACE), macrophage infl amma-
deposits) are other characteristic findings. In many tion factor protein (MIP - 1 β ) and ferritin are also
cases, bone deposits cause bone pain and pathologi- elevated.