Page 141 - Essential Haematology
P. 141
Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes / 127
Lymphocytes are the immunologically competent are generated are the lymph nodes, spleen and lym-
cells that assist the phagocytes in defence of the phoid tissues of the alimentary and respiratory
body against infection and other foreign invasion tracts.
(Fig. 9.1 ). Two unique features characteristic of the
immune system are the ability to generate antigenic
B and T l ymphocytes
specifi city and the phenomenon of immunological
memory . A complete description of the functions Th e immune response depends upon two types of
of lymphocytes is beyond the scope of this book, lymphocytes, B and T cells (Table 9.1 ), which
but information essential to an understanding derive from the haemopoietic stem cell. B cells
of the diseases of the lymphoid system, and of the mature in the bone marrow and circulate in the
role of lymphocytes in haematological diseases, is peripheral blood until they undergo recognition of
included here. antigen. The B - cell receptor is membrane - bound
immunoglobulin and after activation this is secreted
as free soluble immunoglobulin. At this point they
Lymphocytes
mature into memory B cells or plasma cells. Th e
In postnatal life, the bone marrow and thymus latter home to the bone marrow and have a charac-
are the primary lymphoid organs in which lym- teristic morphology with an eccentric round nucleus
phocytes develop (Fig. 9.2 ). Th e secondary lym- with a ‘ clock - face ’ chromatin pattern and strongly
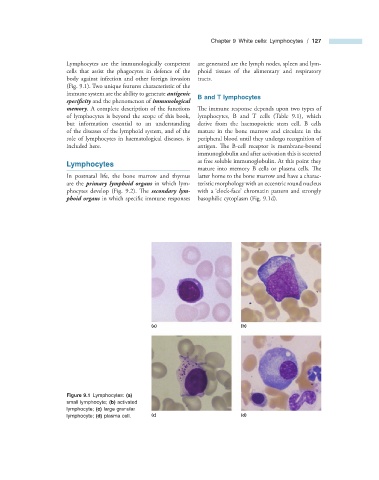
phoid organs in which specific immune responses basophilic cytoplasm (Fig. 9.1 d).
(a) (b)
Figure 9.1 Lymphocytes: (a)
small lymphocyte; (b) activated
lymphocyte; (c) large granular
lymphocyte; (d) plasma cell. (c) (d)