Page 143 - Essential Haematology
P. 143
Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes / 129
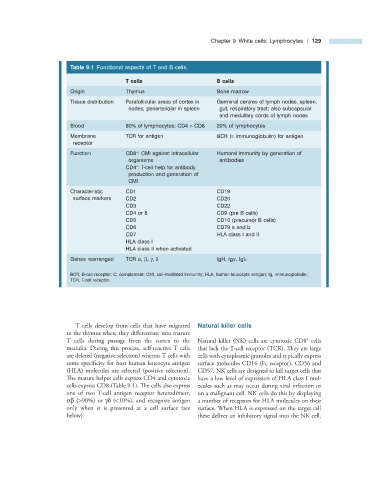
Table 9.1 Functional aspects of T and B cells.
T cells B cells
Origin Thymus Bone marrow
Tissue distribution Parafollicular areas of cortex in Germinal centres of lymph nodes, spleen,
nodes, periarteriolar in spleen gut, respiratory tract; also subcapsular
and medullary cords of lymph nodes
Blood 80% of lymphocytes; CD4 > CD8 20% of lymphocytes
Membrane TCR for antigen BCR ( = immunoglobulin) for antigen
receptor
+
Function CD8 : CMI against intracellular Humoral immunity by generation of
organisms antibodies
+
CD4 : T - cell help for antibody
production and generation of
CMI
Characteristic CD1 CD19
surface markers CD2 CD20
CD3 CD22
CD4 or 8 CD9 (pre B cells)
CD5 CD10 (precursor B cells)
CD6 CD79 a and b
CD7 HLA class I and II
HLA class I
HLA class II when activated
Genes rearranged TCR α , β , γ , δ IgH, Ig κ , Ig λ
BCR, B - cell receptor; C, complement; CMI, cell - mediated immunity; HLA, human leucocyte antigen; Ig, immunoglobulin;
TCR, T - cell receptor.
T cells develop from cells that have migrated Natural k iller c ells
to the thymus where they differentiate into mature
+
T cells during passage from the cortex to the Natural killer (NK) cells are cytotoxic CD8 cells
medulla. During this process, self - reactive T cells that lack the T - cell receptor (TCR). They are large
are deleted (negative selection) whereas T cells with cells with cytoplasmic granules and typically express
some specificity for host human leucocyte antigen surface molecules CD16 (Fc receptor), CD56 and
(HLA) molecules are selected (positive selection). CD57. NK cells are designed to kill target cells that
The mature helper cells express CD4 and cytotoxic have a low level of expression of HLA class I mol-
cells express CD8 (Table 9.1 ). The cells also express ecules such as may occur during viral infection or
one of two T - cell antigen receptor heterodimers, on a malignant cell. NK cells do this by displaying
α β ( > 90%) or γ δ ( < 10%), and recognize antigen a number of receptors for HLA molecules on their
only when it is presented at a cell surface (see surface. When HLA is expressed on the target cell
below). these deliver an inhibitory signal into the NK cell.