Page 148 - Essential Haematology
P. 148
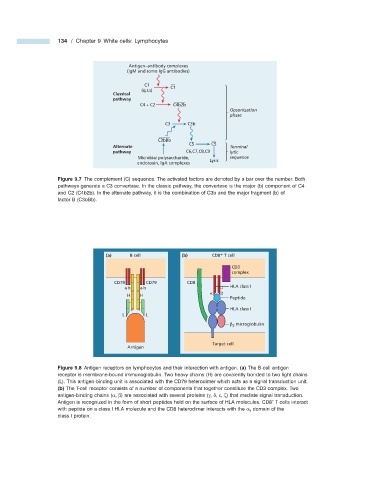
134 / Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes
Antigen–antibody complexes
(IgM and some IgG antibodies)
C1 C1
(q,r,s)
Classical
pathway
C4 + C2 C4b2b
Opsonization
phase
C3 C3b
C3bBb
C5 C5
Alternate Terminal
pathway C6,C7,C8,C9 lytic
Microbial polysaccharide, sequence
endotoxin, IgA complexes Lysis
Figure 9.7 The complement (C) sequence. The activated factors are denoted by a bar over the number. Both
pathways generate a C3 convertase. In the classic pathway, the convertase is the major (b) component of C4
and C2 (C4b2b). In the alternate pathway, it is the combination of C3b and the major fragment (b) of
factor B (C3bBb).
+
(a) B cell (b) CD8 T cell
CD3
complex
CD79 CD79 CD8
a b a b HLA class I
α β
H H
Peptide
HLA class I
L L
β 2 microglobulin
Target cell
Antigen
Figure 9.8 Antigen receptors on lymphocytes and their interaction with antigen. (a) The B - cell antigen
receptor is membrane - bound immunoglobulin. Two heavy chains (H) are covalently bonded to two light chains
(L). This antigen - binding unit is associated with the CD79 heterodimer which acts as a signal transduction unit.
(b) The T - cell receptor consists of a number of components that together constitute the CD3 complex. Two
antigen - binding chains ( α , β ) are associated with several proteins ( γ , δ , ε , ζ ) that mediate signal transduction.
+
Antigen is recognized in the form of short peptides held on the surface of HLA molecules. CD8 T cells interact
domain of the
with peptide on a class I HLA molecule and the CD8 heterodimer interacts with the α 3
class I protein.