Page 150 - Essential Haematology
P. 150
136 / Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes
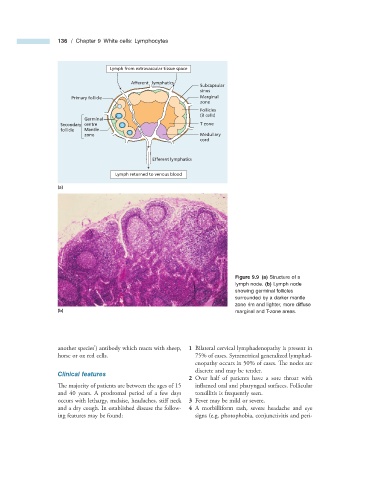
Lymph from extravascular tissue space
Afferent lymphatics
Subcapsular
sinus
Primary follicle Marginal
zone
Follicles
(B cells)
Germinal
Secondary centre T zone
follicle Mantle
zone Medullary
cord
Efferent lymphatics
Lymph returned to venous blood
(a)
Figure 9.9 (a) Structure of a
lymph node. (b) Lymph node
showing germinal follicles
surrounded by a darker mantle
zone rim and lighter, more diffuse
(b) marginal and T - zone areas.
another species ’ ) antibody which reacts with sheep, 1 Bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy is present in
horse or ox red cells. 75% of cases. Symmetrical generalized lymphad-
enopathy occurs in 50% of cases. The nodes are
discrete and may be tender.
Clinical f eatures
2 Over half of patients have a sore throat with
The majority of patients are between the ages of 15 inflamed oral and pharyngeal surfaces. Follicular
and 40 years. A prodromal period of a few days tonsillitis is frequently seen.
occurs with lethargy, malaise, headaches, stiff neck 3 Fever may be mild or severe.
and a dry cough. In established disease the follow- 4 A morbilliform rash, severe headache and eye
ing features may be found: signs (e.g. photophobia, conjunctivitis and peri-