Page 147 - Essential Haematology
P. 147
Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes / 133
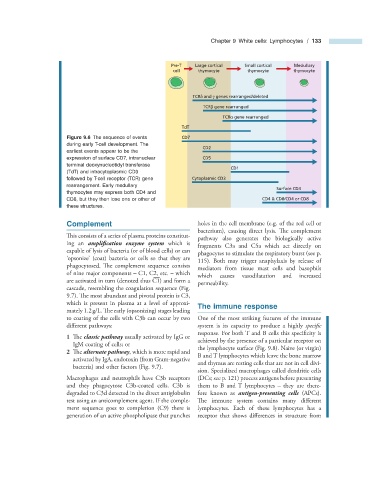
Pre-T Large cortical Small cortical Medullary
cell thymocyte thymocyte thymocyte
TCRδ and γ genes rearranged/deleted
TCRβ gene rearranged
TCRα gene rearranged
TdT
Figure 9.6 The sequence of events CD7
during early T - cell development. The
CD2
earliest events appear to be the
expression of surface CD7, intranuclear CD5
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
CD1
(TdT) and intracytoplasmic CD3
followed by T - cell receptor (TCR) gene Cytoplasmic CD3
rearrangement. Early medullary
Surface CD3
thymocytes may express both CD4 and
CD8, but they then lose one or other of CD4 & CD8/CD4 or CD8
these structures.
Complement holes in the cell membrane (e.g. of the red cell or
bacterium), causing direct lysis. Th e complement
This consists of a series of plasma proteins constitut-
pathway also generates the biologically active
ing an amplification enzyme system which is
fragments C3a and C5a which act directly on
capable of lysis of bacteria (or of blood cells) or can
phagocytes to stimulate the respiratory burst (see p.
‘ opsonize ’ (coat) bacteria or cells so that they are
115) . Both may trigger anaphylaxis by release of
phagocytosed. The complement sequence consists
mediators from tissue mast cells and basophils
of nine major components – C1, C2, etc. – which
— which causes vasodilatation and increased
are activated in turn (denoted thus C1) and form a
permeability.
cascade, resembling the coagulation sequence (Fig.
9.7 ). The most abundant and pivotal protein is C3,
which is present in plasma at a level of approxi- The i mmune r esponse
mately 1.2 g/L. The early (opsonizing) stages leading
to coating of the cells with C3b can occur by two One of the most striking features of the immune
diff erent pathways: system is its capacity to produce a highly specifi c
response. For both T and B cells this specifi city is
1 Th e classic pathway usually activated by IgG or
achieved by the presence of a particular receptor on
IgM coating of cells; or
the lymphocyte surface (Fig. 9.8 ). Naive (or virgin)
2 Th e alternate pathway , which is more rapid and
B and T lymphocytes which leave the bone marrow
activated by IgA, endotoxin (from Gram - negative
and thymus are resting cells that are not in cell divi-
bacteria) and other factors (Fig. 9.7 ).
sion. Specialized macrophages called dendritic cells
Macrophages and neutrophils have C3b receptors (DCs; see p. 121) process antigens before presenting
and they phagocytose C3b - coated cells. C3b is them to B and T lymphocytes – they are there-
degraded to C3d detected in the direct antiglobulin fore known as antigen - presenting cells (APCs).
test using an anticomplement agent . If the comple- The immune system contains many diff erent
ment sequence goes to completion (C9) there is lymphocytes. Each of these lymphocytes has a
generation of an active phospholipase that punches receptor that shows differences in structure from