Page 144 - Essential Haematology
P. 144
130 / Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes
When HLA molecules are absent on the target cell of normal serum immunoglobulin and is further
this inhibitory signal is lost and the NK cell can subdivided into four subclasses : IgG 1 , IgG 2 , IgG 3
then kill its target. In addition, NK cells display and IgG 4 . IgA is subdivided into two types.
antibody - dependent cell - mediated cytotoxicity IgM is usually produced first in response to
(ADCC). In this, antibody binds to antigen on the antigen, IgG subsequently and for a more
surface of the target cell and then NK cells bind to prolonged period. The same cell can switch from
the Fc portion of the bound antibody and kill the IgM to IgG, or to IgA or IgE synthesis. IgA is the
target cell. main immunoglobulin in secretions, particularly
of the gastrointestinal tract. IgD and IgE (involved
in delayed hypersensitivity reactions) are minor
Lymphocyte c irculation
fractions. Some important properties of the three
Lymphocytes in the peripheral blood migrate main immunoglobulin subclasses are summarized
through post - capillary venules into the substance in Table 9.2 .
of the lymph nodes or into the spleen or bone The immunoglobulins are all made up of the
marrow. T cells home to the perifollicular zones of same basic structure (Fig. 9.3 ) consisting of two
the cortical areas of lymph nodes (paracortical areas) heavy chains which are called gamma ( γ ) in IgG,
(Fig. 9.2 ) and to the periarteriolar sheaths sur- alpha ( α ) in IgA, mu ( μ ) in IgM, delta ( δ ) in IgD
rounding the central arterioles of the spleen. B cells and epsilon ( ε ) in IgE, and two light chains – kappa
selectively accumulate in follicles of the lymph ( κ ) or lambda ( λ ) – which are common to all fi ve
nodes and spleen. Lymphocytes return to the immunoglobulins. The heavy and light chains each
peripheral blood via the efferent lymphatic stream have highly variable regions which give the immu-
and the thoracic duct. CD4 helper cells predomi- noglobulin specificity, and constant regions in
nate in normal peripheral blood and germinal which there is virtual complete correspondence in
centres, but in the marrow and gut the major T - cell amino acid sequence in all antibodies of a given
subpopulation is CD8 positive. isotype (e.g. IgA, IgG) or isotype subclass (e.g. IgG 1 ,
IgG 2 ). IgG antibody can be broken into a constant
Fc fragment and two highly variable Fab fragments.
Immunoglobulins
IgM molecules are much larger because they consist
These are a group of proteins produced by plasma of fi ve subunits.
cells and B lymphocytes that bind to antigen. Th ey The main role of immunoglobulins is defence of
are divided into five subclasses or isotypes : immu- the body against foreign organisms. However, they
noglobulin G (IgG), IgA, IgM, IgD and IgE. IgG, also have a vital role in the pathogenesis of a number
the most common, contributes approximately 80% of haematological disorders. Secretion of a specifi c
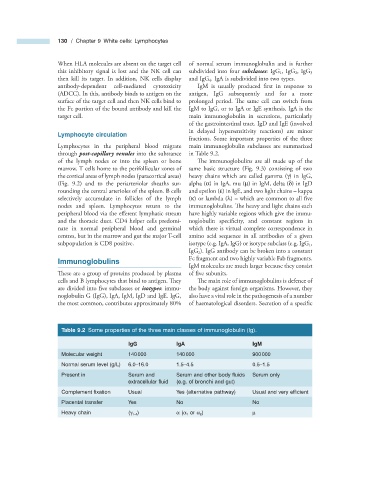
Table 9.2 Some properties of the three main classes of immunoglobulin (Ig).
IgG IgA IgM
Molecular weight 140 000 140 000 900 000
Normal serum level (g/L) 6.0 – 16.0 1.5 – 4.5 0.5 – 1.5
Present in Serum and Serum and other body fl uids Serum only
extracellular fl uid (e.g. of bronchi and gut)
Complement fi xation Usual Yes (alternative pathway) Usual and very effi cient
Placental transfer Yes No No
Heavy chain ( γ 1 – 4 ) α ( α 1 or α 2 ) μ