Page 245 - Essential Haematology
P. 245
Chapter 17 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia / 231
100 72%
Cumulative incidence of relapse 60 43% 23%
80
MRD+ (≥1%) n = 9
MRD+ (≥0.1% – <1%) n = 14
40
MRD+ (<0.1%) n = 19
20
10%
MRD– n = 123
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Years
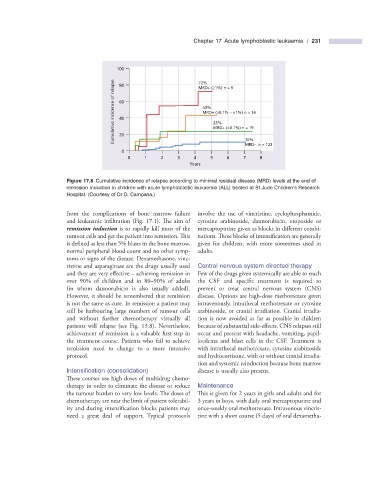
Figure 17.8 Cumulative incidence of relapse according to minimal residual disease (MRD) levels at the end of
remission induction in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) treated at St Jude Children ’ s Research
Hospital. (Courtesy of Dr D. Campana.)
from the complications of bone marrow failure involve the use of vincristine, cyclophosphamide,
and leukaemic infiltration (Fig. 17.1 ). The aim of cytosine arabinoside, daunorubicin, etoposide or
remission induction is to rapidly kill most of the mercaptopurine given as blocks in diff erent combi-
tumour cells and get the patient into remission. Th is nations. Three blocks of intensifi cation are generally
is defined as less than 5% blasts in the bone marrow, given for children, with more sometimes used in
normal peripheral blood count and no other symp- adults.
toms or signs of the disease. Dexamethasone, vinc-
ristine and asparaginase are the drugs usually used Central n ervous s ystem d irected t herapy
and they are very eff ective – achieving remission in Few of the drugs given systemically are able to reach
over 90% of children and in 80 – 90% of adults the CSF and specific treatment is required to
(in whom daunorubicin is also usually added). prevent or treat central nervous system (CNS)
However, it should be remembered that remission disease. Options are high - dose methotrexate given
is not the same as cure. In remission a patient may intravenously, intrathecal methotrexate or cytosine
still be harbouring large numbers of tumour cells arabinoside, or cranial irradiation. Cranial irradia-
and without further chemotherapy virtually all tion is now avoided as far as possible in children
patients will relapse (see Fig. 13.8 ). Nevertheless, because of substantial side - effects. CNS relapses still
achievement of remission is a valuable first step in occur and present with headache, vomiting, papil-
the treatment course. Patients who fail to achieve loedema and blast cells in the CSF. Treatment is
remission need to change to a more intensive with intrathecal methotrexate, cytosine arabinoside
protocol. and hydrocortisone, with or without cranial irradia-
tion and systemic reinduction because bone marrow
Intensifi cation ( c onsolidation) disease is usually also present.
These courses use high doses of multidrug chemo-
therapy in order to eliminate the disease or reduce Maintenance
the tumour burden to very low levels. The doses of This is given for 2 years in girls and adults and for
chemotherapy are near the limit of patient tolerabil- 3 years in boys, with daily oral mercaptopurine and
ity and during intensification blocks patients may once - weekly oral methotrexate. Intravenous vincris-
need a great deal of support. Typical protocols tine with a short course (5 days) of oral dexametha-