Page 240 - Essential Haematology
P. 240
226 / Chapter 17 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
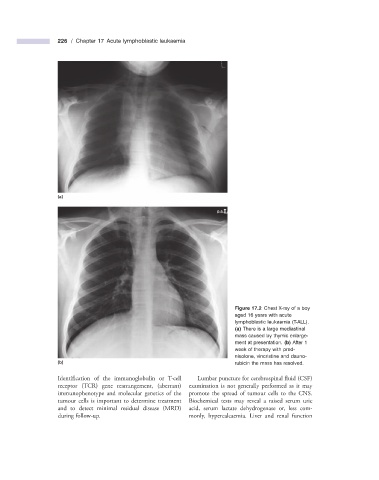
(a)
Figure 17.2 Chest X - ray of a boy
aged 16 years with acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia (T - ALL).
(a) There is a large mediastinal
mass caused by thymic enlarge-
ment at presentation. (b) After 1
week of therapy with pred-
nisolone, vincristine and dauno-
(b) rubicin the mass has resolved.
Identification of the immunoglobulin or T - cell Lumbar puncture for cerebrospinal fl uid (CSF)
receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement, (aberrant) examination is not generally performed as it may
immunophenotype and molecular genetics of the promote the spread of tumour cells to the CNS.
tumour cells is important to determine treatment Biochemical tests may reveal a raised serum uric
and to detect minimal residual disease (MRD) acid, serum lactate dehydrogenase or, less com-
during follow - up. monly, hypercalcaemia. Liver and renal function