Page 239 - Essential Haematology
P. 239
Chapter 17 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia / 225
(a) (b)
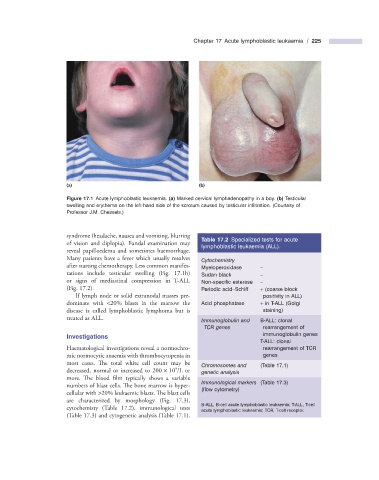
Figure 17.1 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. (a) Marked cervical lymphadenopathy in a boy. (b) Testicular
swelling and erythema on the left - hand side of the scrotum caused by testicular infi ltration. (Courtesy of
Professor J.M. Chessels.)
syndrome (headache, nausea and vomiting, blurring
Table 17.2 Specialized tests for acute
of vision and diplopia). Fundal examination may
lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL).
reveal papilloedema and sometimes haemorrhage.
Many patients have a fever which usually resolves Cytochemistry
after starting chemotherapy. Less common manifes- Myeloperoxidase −
tations include testicular swelling (Fig. 17.1 b) Sudan black −
or signs of mediastinal compression in T - ALL Non - specifi c esterase −
(Fig. 17.2 ). Periodic acid – Schiff + (coarse block
If lymph node or solid extranodal masses pre- positivity in ALL)
dominate with < 20% blasts in the marrow the Acid phosphatase + in T - ALL (Golgi
disease is called lymphoblastic lymphoma but is staining)
treated as ALL. Immunoglobulin and B - ALL: clonal
TCR genes rearrangement of
Investigations immunoglobulin genes
T - ALL: clonal
Haematological investigations reveal a normochro- rearrangement of TCR
mic normocytic anaemia with thrombocytopenia in genes
most cases. The total white cell count may be Chromosomes and (Table 17.1 )
9
decreased, normal or increased to 200 × 10 /L or genetic analysis
more. The blood film typically shows a variable
Immunological markers (Table 17.3 )
numbers of blast cells. The bone marrow is hyper-
(fl ow cytometry)
cellular with > 20% leukaemic blasts. The blast cells
are characterized by morphology (Fig. 17.3 ),
B - ALL, B - cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; T - ALL, T - cell
cytochemisty (Table 17.2 ), immunological tests
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; TCR, T - cell receptor.
(Table 17.3 ) and cytogenetic analysis (Table 17.1 ).