Page 242 - Essential Haematology
P. 242
228 / Chapter 17 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
AML1 translocation. The AML1 protein plays an nosis. Translocations of chromosome 11q23 involve
important part in transcriptional control of haemo- the MLL gene and are seen particularly in cases of
poiesis and is repressed by the TEL - AML1 fusion infant leukaemia. Using more sensitive molecular
protein. genetic tests, as well as fl uorescence in situ hydridi-
The frequency of the Philadelphia translocation zation (FISH) analysis, some cases normal by
t(9; 22) increases with age and carries a poor prog- conventional cytogenetic testing are found to
have fusion genes, e.g BCR - ABL1 or other genetic
abnormalities. These molecular genetic changes
Table 17.3 Immunological markers for carry prognostic significance whether or not a cor-
classifi cation of acute lymphoblastic (ALL) responding chromosomal change is present.
leukaemia. T - ALL accounts for 15% of childhood and 25%
of adult ALL and the clinical picture is often domi-
ALL nated by a very high white cell count, mediastinal
Marker B T
mass or pleural effusion. TCR (and in 20% the IGH
B lineage gene) show clonal rearrangement. Cytogenetic
CD19 + − changes often involve the TCR loci with diff erent
cCD22 + − partner genes. The majority of cases have acquired
cCD79a + − genetic abnormalities that lead to constitutive acti-
CD10 + or − − vation of the NOTCH signalling pathway and drugs
cIg + (pre - B) − that target these abnormalities are being developed
sIg − − (Fig. 17.5 ).
TdT + +
T lineage
Treatment
CD7 − +
cCD3 − + This may be conveniently divided into supportive
CD2 − + and specifi c treatment.
TdT + +
General s upportive t herapy
c, Cytoplasmic; S, surface.
* B - ALL resembles precursor B - ALL immunologically but General supportive therapy for bone marrow failure
has surface immunoglobulin (Ig) and is terminal
−
deoxynucleotidyl transferase negative (TdT ). is described in Chapter 12 and includes the inser-
tion of a central venous cannula, blood product
Infants Children Adults
Ph/BCR-ABL1 Hyperdiploidy TEL-AML1 11q23/MLL Others
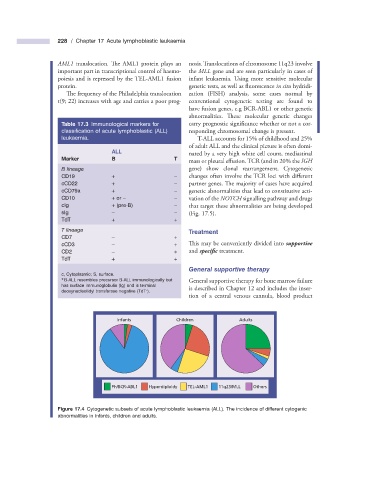
Figure 17.4 Cytogenetic subsets of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL). The incidence of different cytogenic
abnormalities in infants, children and adults.