Page 246 - Essential Haematology
P. 246
232 / Chapter 17 Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
sone is added at monthly or 3 - monthly (in adults) Specifi c t herapy of ALL in a dults
intervals. The value of tests for MRD at the end of
induction or during consolidation is being explored Treatment for ALL in adults has proven challenging
in trials in which the intensity of consolidation compared to the great successes that have been
or maintenance therapy is reduced in those who observed in childhood therapy. The initial control
rapidly become MRD negative, whereas more of the leukaemia (remission induction) is compara-
intensified therapy, or even stem cell transplantation ble in both groups but the rate of disease relapse is
(SCT), is given to those with persistent MRD. much higher in adults. Although cure rates in chil-
There is a high risk of varicella or measles during dren now approach 90%, no more than 40% of
maintenance therapy in children who lack immu- adult patients remain free of leukaemia after 5 years
nity to these viruses. If exposure to these infections and this rate is much lower in older patients. A
occurs, prophylactic immunoglobulin should be significant factor is that the genetic subtypes of the
given. In addition, oral co - trimoxazole is given to ALL differ according to age. Hyperdiploidy and
reduce the risk of Pneumocystis carinii . t(12; 21), which carry a good prognosis and together
make up 50% of childhood cases, are both rare in
adult patients. In contrast, the presence of the
Treatment of r elapse
Philadelphia chromosome (Ph + ALL) becomes
If relapse occurs during or soon after maintenance more common with age (Fig. 17.4 ).
chemotherapy the outlook is poor. Reinduction An additional factor that has contributed to the
with combination chemotherapy including novel relatively poor outcome for ALL in adults is the
drugs such as clofarabine may help. Chemotherapy lower doses of chemotherapy that have traditionally
is usually followed, where possible, by allogeneic been used in adult patients. This is now being
SCT. If relapse occurs after years off all therapy the addressed in younger adult patients where high
outlook is better and reinduction, consolidation intensity chemotherapy regimens are being intro-
and maintenance therapy are given. Allogeneic SCT duced. The presence of MRD after 3 months or
may also be indicated. more of therapy is an unfavourable prognostic sign.
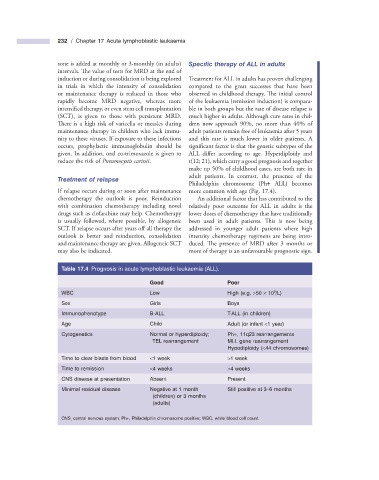
Table 17.4 Prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL).
Good Poor
9
WBC Low High (e.g. > 50 × 10 /L)
Sex Girls Boys
Immunophenotype B - ALL T - ALL (in children)
Age Child Adult (or infant < 1 year)
Cytogenetics Normal or hyperdiploidy; Ph + , 11q23 rearrangements
TEL rearrangement MLL gene rearrangement
Hypodiploidy ( < 44 chromosomes)
Time to clear blasts from blood < 1 week > 1 week
Time to remission < 4 weeks > 4 weeks
CNS disease at presentation Absent Present
Minimal residual disease Negative at 1 month Still positive at 3 – 6 months
(children) or 3 months
(adults)
CNS, central nervous system; Ph + , Philadelphia chromosome positive; WBC, white blood cell count.