Page 264 - Essential Haematology
P. 264
250 / Chapter 19 Hodgkin lymphoma
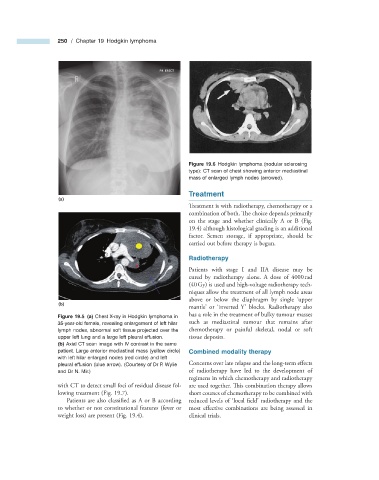
Figure 19.6 Hodgkin lymphoma (nodular sclerosing
type): CT scan of chest showing anterior mediastinal
mass of enlarged lymph nodes (arrowed).
Treatment
(a)
Treatment is with radiotherapy, chemotherapy or a
combination of both. The choice depends primarily
on the stage and whether clinically A or B (Fig.
19.4 ) although histological grading is an additional
factor. Semen storage, if appropriate, should be
carried out before therapy is begun.
Radiotherapy
Patients with stage I and IIA disease may be
cured by radiotherapy alone. A dose of 4000 rad
(40 Gy) is used and high - voltage radiotherapy tech-
niques allow the treatment of all lymph node areas
‘
above or below the diaphragm by single upper
(b)
mantle ’ or ‘ inverted Y ’ blocks. Radiotherapy also
has a role in the treatment of bulky tumour masses
Figure 19.5 (a) Chest X - ray in Hodgkin lymphoma in
35 - year - old female, revealing enlargement of left hilar such as mediastinal tumour that remains after
lymph nodes, abnormal soft tissue projected over the chemotherapy or painful skeletal, nodal or soft
upper left lung and a large left pleural effusion. tissue deposits.
(b) Axial CT scan image with IV contrast in the same
patient. Large anterior mediastinal mass (yellow circle) Combined m odality t herapy
with left hilar enlarged nodes (red circle) and left
pleural effusion (blue arrow). (Courtesy of Dr P. Wylie Concerns over late relapse and the long - term eff ects
and Dr N. Mir.) of radiotherapy have led to the development of
regimens in which chemotherapy and radiotherapy
with CT to detect small foci of residual disease fol- are used together. This combination therapy allows
lowing treatment (Fig. 19.7 ). short courses of chemotherapy to be combined with
Patients are also classified as A or B according reduced levels of ‘ local field ’ radiotherapy and the
to whether or not constitutional features (fever or most effective combinations are being assessed in
weight loss) are present (Fig. 19.4 ). clinical trials.