Page 265 - Essential Haematology
P. 265
Chapter 19 Hodgkin lymphoma / 251
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
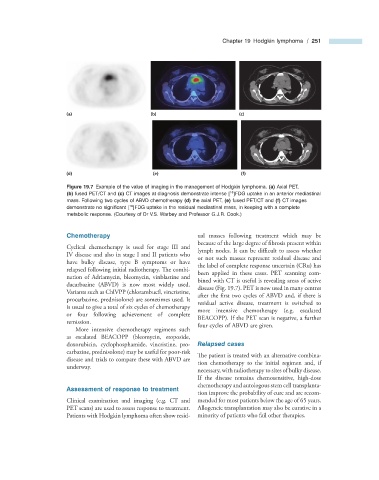
Figure 19.7 Example of the value of imaging in the management of Hodgkin lymphoma. (a) Axial PET,
18
(b) fused PET/CT and (c) CT images at diagnosis demonstrate intense [ ]FDG uptake in an anterior mediastinal
mass. Following two cycles of ABVD chemotherapy (d) the axial PET, (e) fused PET/CT and (f) CT images
18
demonstrate no signifi cant [ ]FDG uptake in the residual mediastinal mass, in keeping with a complete
metabolic response. (Courtesy of Dr V.S. Warbey and Professor G.J.R. Cook.)
Chemotherapy ual masses following treatment which may be
because of the large degree of fibrosis present within
Cyclical chemotherapy is used for stage III and lymph nodes. It can be difficult to assess whether
IV disease and also in stage I and II patients who or not such masses represent residual disease and
have bulky disease, type B symptoms or have the label of complete response uncertain (CRu) has
relapsed following initial radiotherapy. Th e combi- been applied in these cases. PET scanning com-
nation of Adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine and bined with CT is useful is revealing areas of active
dacarbazine (ABVD) is now most widely used. disease (Fig. 19.7 ). PET is now used in many centres
Variants such as ChlVPP (chlorambucil, vincristine, after the first two cycles of ABVD and, if there is
procarbazine, prednisolone) are sometimes used. It residual active disease, treatment is switched to
is usual to give a total of six cycles of chemotherapy more intensive chemotherapy (e.g. escalated
or four following achievement of complete BEACOPP). If the PET scan is negative, a further
remission. four cycles of ABVD are given.
More intensive chemotherapy regimens such
as escalated BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide,
doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, pro- Relapsed c ases
carbazine, prednisolone) may be useful for poor - risk The patient is treated with an alternative combina-
disease and trials to compare these with ABVD are tion chemotherapy to the initial regimen and, if
underway.
necessary, with radiotherapy to sites of bulky disease.
If the disease remains chemosensitive, high - dose
chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplanta-
Assessment of r esponse to t reatment
tion improve the probability of cure and are recom-
Clinical examination and imaging (e.g. CT and mended for most patients below the age of 65 years.
PET scans) are used to assess response to treatment. Allogeneic transplantation may also be curative in a
Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma often show resid- minority of patients who fail other therapies.