Page 280 - Essential Haematology
P. 280
266 / Chapter 20 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
other low - grade lymphomas such as follicular lym- sometimes associated with a leukaemic phase.
phoma. Radiotherapy and rituximab are also used. Around 10% of patients have initially localized
(Stage 1) disease and may achieve cure with radio-
therapy alone. Those with disseminated (Stage
Follicular l ymphoma
II – IV) disease are generally not treated in the
This represents around 25% of NHL with a median absence of symptoms ( watch and wait ’ ) but treat-
‘
age of onset of 60 years. It is associated with the ment is introduced when complications occur. At
t(14; 18) translocation in the great majority of cases the current time, chemotherapy is not a curative
(Figs 20.14 and 20.15 ). The translocation leads to option. Therapy is usually based on monthly courses
constitutive expression of the BCL - 2 gene with of rituximab, in combination with cyclophospha-
increased survival of cells because of reduced mide, vincristine and prednisolone (R - CVP), or
apoptosis. rituximab with bendamustine or chlorambucil.
Patients are likely to be middle - aged or elderly These regimens can provide clinical responses in up
and their disease is often characterized by a benign to 90% of patients and usually achieve a remission
course for many years. The median survival from of several years. Rituximab infusions can also be
diagnosis is approximately 10 years. Th e histological given as maintenance therapy, and are typically
appearances are graded as I – III according to the administered every 2 – 6 months as the antibody has
relative proportion of centrocytes and centroblasts, a long half - life in the circulation.
Grade IIIb patients, who are treated according to Disease relapse for stage II – IV disease is almost
diffuse large B - cell lymphoma (DLBCL) guidelines inevitable and is usually treated initially with similar
(see below), having the worst prognosis. Bone chemotherapy regimens followed by rituximab
marrow involvement is frequent. maintenance. Over time the disease becomes
Presentation is usually with painless lymphade- increasingly difficult to control and more intensive
nopathy, often widespread, and the majority of chemotherapy or radiolabelled antibody therapy
patients will have stage III or IV disease. Relatively (anti - CD20) may be considered. Autologous SCT
benign types may present rarely as polyps in the may be valuable in patients with a history of at least
duodenum, in the skin, or in children. However, one relapse and allogeneic SCT using reduced
sudden transformation may occur at a rate of about intensity protocols offers the prospect of cure for
3% a year to aggressive diffuse tumours which are some patients.
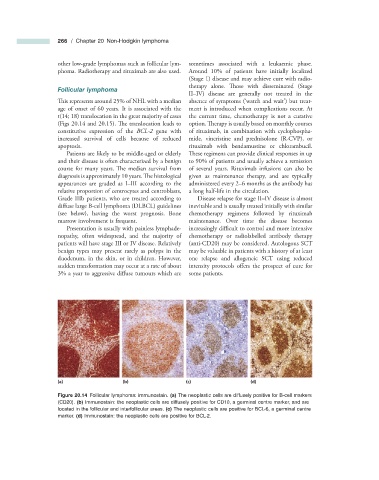
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 20.14 Follicular lymphoma: immunostain. (a) The neoplastic cells are diffusely positive for B - cell markers
(CD20). (b) Immunostain: the neoplastic cells are diffusely positive for CD10, a germinal centre marker, and are
located in the follicular and interfollicular areas. (c) The neoplastic cells are positive for BCL - 6, a germinal centre
marker. (d) Immunostain: the neoplastic cells are positive for BCL - 2.