Page 276 - Essential Haematology
P. 276
262 / Chapter 20 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
a bleeding tendency may result from macroglobulin Diagnosis is made by the finding of a mono-
interference with coagulation factors and platelet clonal serum IgM together with bone marrow or
function. Neurological symptoms, neuropathy, dys- lymph node infiltration with lymphoplasmacytoid
pnoea and heart failure may be presenting symp- cells (Fig. 20.11 ). The erythrocyte sedimentation
toms. Moderate lymphadenopathy and enlargement rate (ESR) is raised and there may be a peripheral
of the liver and spleen are frequently seen. blood lymphocytosis.
100
90
ABC DLBCL
80
Probability 70
60
50
GCB DLBCL 40
Probability 30
20
10
0 Gene Name
FLJ00050
FOXP1 transcription factor
LOC 152137
SH3BP5 signaling factor
4.0 •IRF4 transcription factor
FLJ39358
•IL-16
2.0 BLNK signaling protein
•CD39
•N-Acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide
BMF proapoptotic BH3-only protein
1.0 Tel transcription factor
•CCND2/Cyclin D2
•Pim-1 kinase
0.5 •Protein Tyr Plase non-receptor type 1
•Immunoglobulin mu
IMAGE:1338044
•CD10
0.25 IMAGE:1338486
KIAA0870
Fold •LRMP/JAW1 ER protein
Relative Never in mitosis gene a-related kinase 6
•BCL-6 transcription factor
Expression •LMO2 transctrption factor
IMAGE: 1334260
ABC DLBCL GCB DLBCL 1D-myo-inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase B
•MYBL1/A-myb transctrption factor
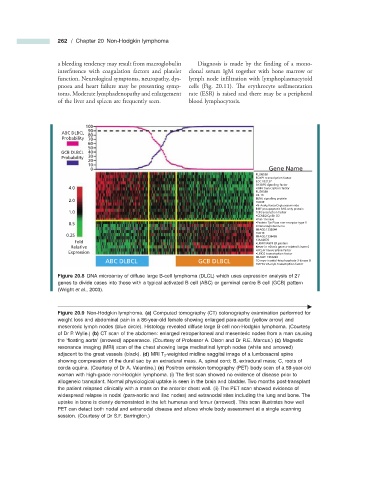
Figure 20.8 DNA microarray of diffuse large B - cell lymphoma (DLCL) which uses expression analysis of 27
genes to divide cases into those with a typical activated B cell (ABC) or germinal centre B cell (GCB) pattern
(Wright et al ., 2003).
Figure 20.9 Non - Hodgkin lymphoma. (a) Computed tomography (CT) colonography examination performed for
weight loss and abdominal pain in a 86 - year - old female showing enlarged para - aortic (yellow arrow) and
mesenteric lymph nodes (blue circle). Histology revealed diffuse large B - cell non - Hodgkin lymphoma. (Courtesy
of Dr P. Wylie.) (b) CT scan of the abdomen: enlarged retroperitoneal and mesenteric nodes from a man causing
the ‘ fl oating aorta ’ (arrowed) appearance. (Courtesy of Professor A. Dixon and Dr R.E. Marcus.) (c) Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the chest showing large mediastinal lymph nodes (white and arrowed)
adjacent to the great vessels (black). (d) MRI T 2 - weighted midline saggital image of a lumbosacral spine
showing compression of the dural sac by an extradural mass. A, spinal cord; B, extradural mass; C, roots of
corda equina. (Courtesy of Dr A. Valentine.) (e) Positron emission tomography (PET) body scan of a 59 - year - old
woman with high - grade non - Hodgkin lymphoma. (i) The fi rst scan showed no evidence of disease prior to
allogeneic transplant. Normal physiological uptake is seen in the brain and bladder. Two months post - transplant
the patient relapsed clinically with a mass on the anterior chest wall. (ii) The PET scan showed evidence of
widespread relapse in nodal (para - aortic and iliac nodes) and extranodal sites including the lung and bone. The
uptake in bone is clearly demonstated in the left humerus and femur (arrowed). This scan illustrates how well
PET can detect both nodal and extranodal disease and allows whole body assessment at a single scanning
session. (Courtesy of Dr S.F. Barrington.)