Page 271 - Essential Haematology
P. 271
Chapter 20 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma / 257
’
structures (Waldeyer s ring) which may cause Investigations
‘
complaints of a sore throat ’ or noisy or obstructed
Histology
breathing.
4 Symptoms due to anaemia , infections due to neu- Lymph node biopsy or trucut biopsy of lymph node
tropenia or purpura with thrombocytopenia may or of other involved tissue (e.g. bone marrow or
be presenting features in patients with diff use extranodal tissue) is the definitive investigation (Figs
bone marrow disease. Cytopenias may also be 20.3 and 20.4 ). Morphological examination is
autoimmune in origin or due to sequestration in assisted by immunophenotypic and, in some cases,
the spleen. Infections may occur as a result of genetic analysis (Table 20.3 ). For B - cell lymphomas,
neutropenia or reduced cell immunity (e.g. expression of either κ or λ light chains confi rms
herpes zoster). clonality and distinguishes the disease from a reac-
5 Abdominal disease The liver and spleen are often tive node (Fig. 20.5 ). A fine needle aspiration may
enlarged and involvement of retroperitoneal or be performed to exclude another cause of lymphad-
mesenteric nodes is frequent. Th e gastrointestinal enopathy (e.g. tuberculosis, carcinoma) but is not
tract is the most commonly involved extranodal useful in establishing a diagnosis of lymphoma.
site after the bone marrow, and patients may
present with acute abdominal symptoms. Laboratory i nvestigations
6 Other organs Skin, brain, testis or thyroid
involvement is not infrequent. The skin is also 1 In advanced disease with marrow involvement
primarily involved in two unusual, closely related there may be anaemia, neutropenia or thrombo-
T - cell lymphomas, mycosis fungoides and S é zary cytopenia (especially if the spleen is enlarged or
syndrome. there are leucoerythroblastic features).
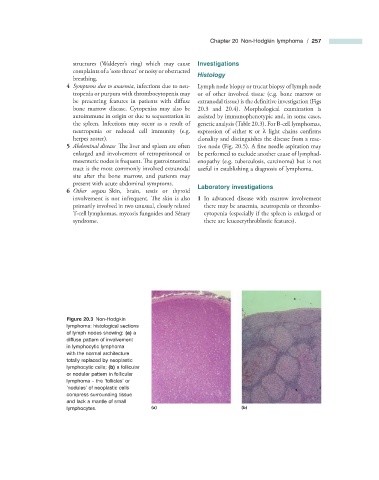
Figure 20.3 Non - Hodgkin
lymphoma: histological sections
of lymph nodes showing: (a) a
diffuse pattern of involvement
in lymphocytic lymphoma
with the normal architecture
totally replaced by neoplastic
lymphocytic cells; (b) a follicular
or nodular pattern in follicular
lymphoma – the ‘ follicles ’ or
‘ nodules ’ of neoplastic cells
compress surrounding tissue
and lack a mantle of small
lymphocytes. (a) (b)