Page 272 - Essential Haematology
P. 272
258 / Chapter 20 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
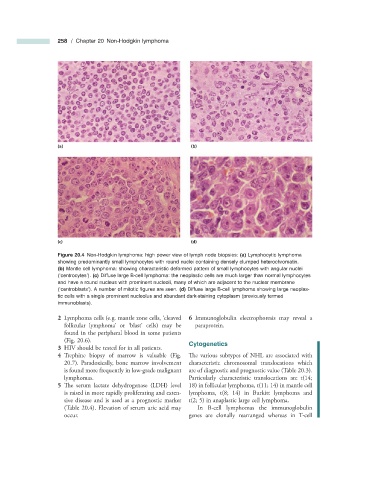
Figure 20.4 Non - Hodgkin lymphoma: high power view of lymph node biopsies: (a) Lymphocytic lymphoma
showing predominantly small lymphocytes with round nuclei containing densely clumped heterochromatin.
(b) Mantle cell lymphoma: showing characteristic deformed pattern of small lymphocytes with angular nuclei
( ‘ centrocytes ’ ). (c) Diffuse large B - cell lymphoma: the neoplastic cells are much larger than normal lymphocytes
and have a round nucleus with prominent nucleoli, many of which are adjacent to the nuclear membrane
( ‘ centroblasts ’ ). A number of mitotic fi gures are seen. (d) Diffuse large B - cell lymphoma showing large neoplas-
tic cells with a single prominent nucleolus and abundant dark - staining cytoplasm (previously termed
immunoblasts).
2 Lymphoma cells (e.g. mantle zone cells, cleaved 6 Immunoglobulin electrophoresis may reveal a
‘
follicular lymphoma ’ or ‘ blast ’ cells) may be paraprotein.
found in the peripheral blood in some patients
(Fig. 20.6 ).
Cytogenetics
3 HIV should be tested for in all patients.
4 Trephine biopsy of marrow is valuable (Fig. The various subtypes of NHL are associated with
20.7 ). Paradoxically, bone marrow involvement characteristic chromosomal translocations which
is found more frequently in low - grade malignant are of diagnostic and prognostic value (Table 20.3 ).
lymphomas. Particularly characteristic translocations are t(14;
5 The serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level 18) in follicular lymphoma, t(11; 14) in mantle cell
is raised in more rapidly proliferating and exten- lymphoma, t(8; 14) in Burkitt lymphoma and
sive disease and is used as a prognostic marker t(2; 5) in anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
(Table 20.4 ). Elevation of serum uric acid may In B - cell lymphomas the immunoglobulin
occur. genes are clonally rearranged whereas in T - cell