Page 282 - Essential Haematology
P. 282
268 / Chapter 20 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
(a) (b) (c)
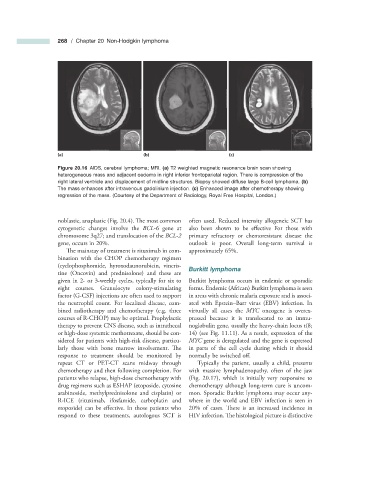
Figure 20.16 AIDS, cerebral lymphoma; MRI. (a) T2 weighted magnetic resonance brain scan showing
heterogeneous mass and adjacent oedema in right inferior frontoparietal region. There is compression of the
right lateral ventricle and displacement of midline structures. Biopsy showed diffuse large B - cell lymphoma. (b)
The mass enhances after intravenous gadolinium injection. (c) Enhanced image after chemotherapy showing
regression of the mass. (Courtesy of the Department of Radiology, Royal Free Hospital, London.)
noblastic, anaplastic (Fig. 20.4 ). The most common often used. Reduced intensity allogeneic SCT has
cytogenetic changes involve the BCL - 6 gene at also been shown to be effective For those with
chromosome 3q27; and translocation of the BCL - 2 primary refractory or chemoresistant disease the
gene, occurs in 20%. outlook is poor. Overall long - term survival is
The mainstay of treatment is rituximab in com- approximately 65%.
bination with the CHOP chemotherapy regimen
(cyclophosphomide, hyroxodaunorubicin, vincris- Burkitt l ymphoma
tine (Oncovin) and prednisolone) and these are
given in 2 - or 3 - weekly cycles, typically for six to Burkitt lymphoma occurs in endemic or sporadic
eight courses. Granulocyte colony - stimulating forms. Endemic (African) Burkitt lymphoma is seen
factor (G - CSF) injections are often used to support in areas with chronic malaria exposure and is associ-
the neutrophil count. For localized disease, com- ated with Epstein – Barr virus (EBV) infection. In
bined radiotherapy and chemotherapy (e.g. three virtually all cases the MYC oncogene is overex-
courses of R - CHOP) may be optimal. Prophylactic pressed because it is translocated to an immu-
therapy to prevent CNS disease, such as intrathecal noglobulin gene, usually the heavy - chain locus t(8;
or high - dose systemic methotrexate, should be con- 14) (see Fig. 11.11 ) . As a result, expression of the
sidered for patients with high - risk disease, particu- MYC gene is deregulated and the gene is expressed
larly those with bone marrow involvement. Th e in parts of the cell cycle during which it should
response to treatment should be monitored by normally be switched off .
repeat CT or PET - CT scans midway through Typically the patient, usually a child, presents
chemotherapy and then following completion. For with massive lymphadenopathy, often of the jaw
patients who relapse, high - dose chemotherapy with (Fig. 20.17 ), which is initially very responsive to
drug regimens such as ESHAP (etoposide, cytosine chemotherapy although long - term cure is uncom-
arabinoside, methylprednisolone and cisplatin) or mon. Sporadic Burkitt lymphoma may occur any-
R - ICE (rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin and where in the world and EBV infection is seen in
etoposide) can be effective. In those patients who 20% of cases. There is an increased incidence in
respond to these treatments, autologous SCT is HIV infection. The histological picture is distinctive