Page 364 - Essential Haematology
P. 364
350 / Chapter 26 Coagulation disorders
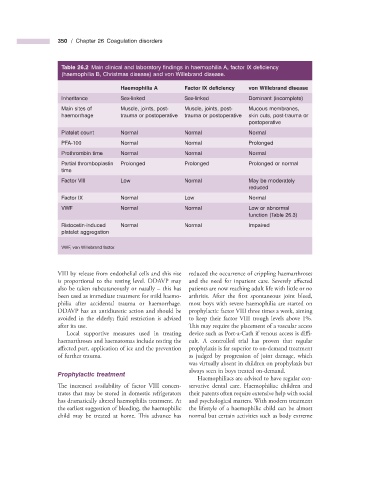
Table 26.2 Main clinical and laboratory fi ndings in haemophilia A , factor IX defi ciency
(haemophilia B , Christmas disease) and von Willebrand disease.
Haemophilia A Factor IX defi ciency von Willebrand disease
Inheritance Sex - linked Sex - linked Dominant (incomplete)
Main sites of Muscle, joints, post - Muscle, joints, post - Mucous membranes,
haemorrhage trauma or postoperative trauma or postoperative skin cuts, post - trauma or
postoperative
Platelet count Normal Normal Normal
PFA - 100 Normal Normal Prolonged
Prothrombin time Normal Normal Normal
Partial thromboplastin Prolonged Prolonged Prolonged or normal
time
Factor VIII Low Normal May be moderately
reduced
Factor IX Normal Low Normal
VWF Normal Normal Low or abnormal
function (Table 26.3 )
Ristocetin - induced Normal Normal Impaired
platelet aggregation
VWF, von Willebrand factor.
VIII by release from endothelial cells and this rise reduced the occurrence of crippling haemarthroses
is proportional to the resting level. DDAVP may and the need for inpatient care. Severely aff ected
also be taken subcutaneously or nasally – this has patients are now reaching adult life with little or no
been used as immediate treatment for mild haemo- arthritis. After the first spontaneous joint bleed,
philia after accidental trauma or haemorrhage. most boys with severe haemophilia are started on
DDAVP has an antidiuretic action and should be prophylactic factor VIII three times a week, aiming
avoided in the elderly; fluid restriction is advised to keep their factor VIII trough levels above 1%.
after its use. This may require the placement of a vascular access
Local supportive measures used in treating device such as Port - a - Cath if venous access is diffi -
haemarthroses and haematomas include resting the cult. A controlled trial has proven that regular
affected part, application of ice and the prevention prophylaxis is far superior to on - demand treatment
of further trauma. as judged by progression of joint damage, which
was virtually absent in children on prophylaxis but
always seen in boys treated on - demand.
Prophylactic t reatment
Haemophiliacs are advised to have regular con-
The increased availability of factor VIII concen- servative dental care. Haemophiliac children and
trates that may be stored in domestic refrigerators their parents often require extensive help with social
has dramatically altered haemophilia treatment. At and psychological matters. With modern treatment
the earliest suggestion of bleeding, the haemophilic the lifestyle of a haemophilic child can be almost
child may be treated at home. This advance has normal but certain activities such as body extreme