Page 367 - Essential Haematology
P. 367
Chapter 26 Coagulation disorders / 353
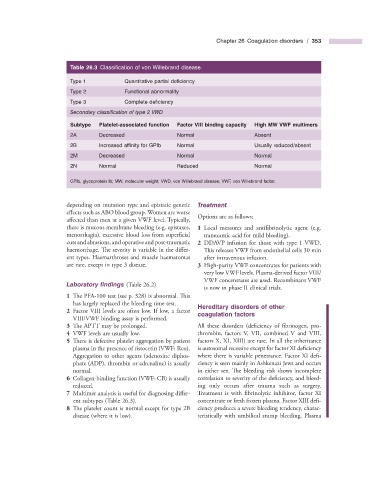
Table 26.3 Classifi cation of von Willebrand disease.
Type 1 Quantitative partial defi ciency
Type 2 Functional abnormality
Type 3 Complete defi ciency
Secondary classifi cation of type 2 VWD
Subtype Platelet - associated function Factor VIII binding capacity High MW VWF multimers
2A Decreased Normal Absent
2B Increased affi nity for GPIb Normal Usually reduced/absent
2M Decreased Normal Normal
2N Normal Reduced Normal
GPIb, glycoprotein Ib; MW, molecular weight; VWD, von Willebrand disease; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
depending on mutation type and epistatic genetic Treatment
effects such as ABO blood group. Women are worse
Options are as follows:
affected than men at a given VWF level. Typically,
there is mucous membrane bleeding (e.g. epistaxes, 1 Local measures and antifibrinolytic agent (e.g.
menorrhagia), excessive blood loss from superfi cial tranexamic acid for mild bleeding).
cuts and abrasions, and operative and post - traumatic 2 DDAVP infusion for those with type 1 VWD.
haemorrhage. The severity is variable in the diff er- This releases VWF from endothelial cells 30 min
ent types. Haemarthroses and muscle haematomas after intravenous infusion.
are rare, except in type 3 disease. 3 High - purity VWF concentrates for patients with
very low VWF levels. Plasma - derived factor VIII/
VWF concentrates are used. Recombinant VWF
Laboratory fi ndings (Table 26.2 )
is now in phase II clinical trials.
1 The PFA - 100 test (see p. 328 ) is abnormal. Th is
has largely replaced the bleeding time test.
Hereditary d isorders of o ther
2 Factor VIII levels are often low. If low, a factor
c oagulation f actors
VIII/VWF binding assay is performed.
3 The APTT may be prolonged. All these disorders (deficiency of fi brinogen, pro-
4 VWF levels are usually low. thrombin, factors V, VII, combined V and VIII,
5 There is defective platelet aggregation by patient factors X, XI, XIII) are rare. In all the inheritance
plasma in the presence of ristocetin (VWF: Rco). is autosomal recessive except for factor XI defi ciency
Aggregation to other agents (adenosine diphos- where there is variable penetrance. Factor XI defi -
phate (ADP), thrombin or adrenaline) is usually ciency is seen mainly in Ashkenazi Jews and occurs
normal. in either sex. The bleeding risk shows incomplete
6 Collagen - binding function (VWF: CB) is usually correlation to severity of the deficiency, and bleed-
reduced. ing only occurs after trauma such as surgery.
7 Multimer analysis is useful for diagnosing diff er- Treatment is with fibrinolytic inhibitor, factor XI
ent subtypes (Table 26.3 ). concentrate or fresh frozen plasma. Factor XIII defi -
8 The platelet count is normal except for type 2B ciency produces a severe bleeding tendency, charac-
disease (where it is low). teristically with umbilical stump bleeding. Plasma