Page 371 - Essential Haematology
P. 371
Chapter 26 Coagulation disorders / 357
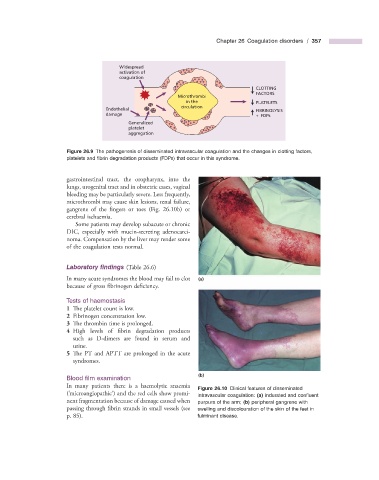
Widespread
activation of
coagulation
CLOTTING
FACTORS
Microthrombi
in the PLATELETS
circulation
Endothelial FIBRINOLYSIS
damage + FDPs
Generalized
platelet
aggregation
Figure 26.9 The pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation and the changes in clotting factors,
platelets and fi brin degradation products (FDPs) that occur in this syndrome.
gastrointestinal tract, the oropharynx, into the
lungs, urogenital tract and in obstetric cases, vaginal
bleeding may be particularly severe. Less frequently,
microthrombi may cause skin lesions, renal failure,
gangrene of the fingers or toes (Fig. 26.10 b) or
cerebral ischaemia.
Some patients may develop subacute or chronic
DIC, especially with mucin - secreting adenocarci-
noma. Compensation by the liver may render some
of the coagulation tests normal.
Laboratory fi ndings (Table 26.6 )
In many acute syndromes the blood may fail to clot (a)
because of gross fi brinogen deficiency.
Tests of h aemostasis
1 The platelet count is low.
2 Fibrinogen concentration low.
3 The thrombin time is prolonged.
4 High levels of fibrin degradation products
such as D - dimers are found in serum and
urine.
5 The PT and APTT are prolonged in the acute
syndromes.
(b)
Blood fi lm e xamination
In many patients there is a haemolytic anaemia
Figure 26.10 Clinical features of disseminated
‘
( microangiopathic ’ ) and the red cells show promi- intravascular coagulation: (a) indurated and confl uent
nent fragmentation because of damage caused when purpura of the arm; (b) peripheral gangrene with
passing through fibrin strands in small vessels (see swelling and discolouration of the skin of the feet in
p. 85 ). fulminant disease.