Page 45 - Essential Haematology
P. 45
Chapter 2 Erythropoiesis and anaemia / 31
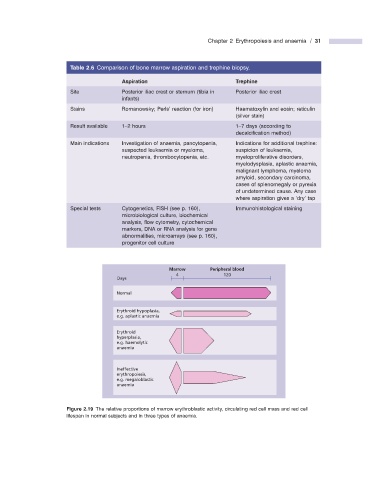
Table 2.6 Comparison of bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy.
Aspiration Trephine
Site Posterior iliac crest or sternum (tibia in Posterior iliac crest
infants)
Stains Romanowsky; Perls ’ reaction (for iron) Haematoxylin and eosin; reticulin
(silver stain)
Result available 1 – 2 hours 1 – 7 days (according to
decalcifi cation method)
Main indications Investigation of anaemia, pancytopenia, Indications for additional trephine:
suspected leukaemia or myeloma, suspicion of leukaemia,
neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, etc. myeloproliferative disorders,
myelodysplasia, aplastic anaemia,
malignant lymphoma, myeloma
amyloid, secondary carcinoma,
cases of splenomegaly or pyrexia
of undetermined cause. Any case
where aspiration gives a ‘ dry ’ tap
Special tests Cytogenetics, FISH (see p. 160 ), Immunohistological staining
microbiological culture, biochemical
analysis, fl ow cytometry, cytochemical
markers, DNA or RNA analysis for gene
abnormalities, microarrays (see p. 160 ),
progenitor cell culture
Marrow Peripheral blood
4 120
Days
Normal
Erythroid hypoplasia,
e.g. aplastic anaemia
Erythroid
hyperplasia,
e.g. haemolytic
anaemia
Ineffective
erythropoiesis,
e.g. megaloblastic
anaemia
Figure 2.19 The relative proportions of marrow erythroblastic activity, circulating red cell mass and red cell
lifespan in normal subjects and in three types of anaemia.