Page 50 - Essential Haematology
P. 50
36 / Chapter 3 Hypochromic anaemias
Table 3.1 The distribution of body iron.
Amount of iron in average adult Male (g) Female (g) Percentage of total
Haemoglobin 2.4 1.7 65
Ferritin and haemosiderin 1.0 (0.3 – 1.5) 0.3 (0 – 1.0) 30
Myoglobin 0.15 0.12 3.5
Haem enzymes (e.g. cytochromes, catalase, 0.02 0.015 0.5
peroxidases, fl avoproteins)
Transferrin - bound iron 0.004 0.003 0.1
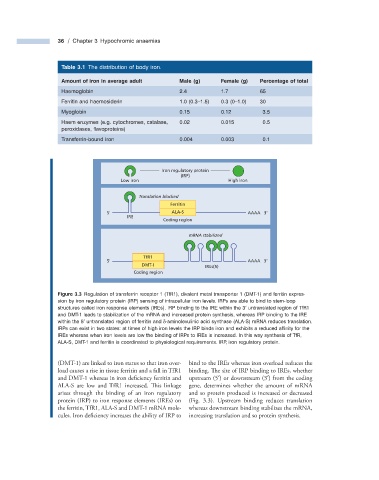
Iron regulatory protein
(IRP)
Low iron High iron
Translation blocked
Ferritin
5' ALA-S AAAA 3'
IRE
Coding region
mRNA stabilized
TfR1
5' AAAA 3'
DMT-I IREs(5)
Coding region
Figure 3.3 Regulation of transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT - 1) and ferritin expres-
sion by iron regulatory protein (IRP) sensing of intracellular iron levels. IRPs are able to bind to stem - loop
′
structures called iron response elements (IREs). IRP binding to the IRE within the 3 untranslated region of TfR1
and DMT - 1 leads to stabilization of the mRNA and increased protein synthesis, whereas IRP binding to the IRE
′
within the 5 untranslated region of ferritin and δ - aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALA - S) mRNA reduces translation.
IRPs can exist in two states: at times of high iron levels the IRP binds iron and exhibits a reduced affi nity for the
IREs whereas when iron levels are low the binding of IRPs to IREs is increased. In this way synthesis of TfR,
ALA - S, DMT - 1 and ferritin is coordinated to physiological requirements. IRP, iron regulatory protein.
(DMT - 1) are linked to iron status so that iron over- bind to the IREs whereas iron overload reduces the
load causes a rise in tissue ferritin and a fall in TfR1 binding. The site of IRP binding to IREs, whether
′
′
and DMT - 1 whereas in iron deficiency ferritin and upstream (5 ) or downstream (3 ) from the coding
ALA - S are low and TfR1 increased. Th is linkage gene, determines whether the amount of mRNA
arises through the binding of an iron regulatory and so protein produced is increased or decreased
protein (IRP) to iron response elements (IREs) on (Fig. 3.3 ). Upstream binding reduces translation
the ferritin, TfR1, ALA - S and DMT - 1 mRNA mole- whereas downstream binding stabilizes the mRNA,
cules. Iron defi ciency increases the ability of IRP to increasing translation and so protein synthesis.