Page 54 - Essential Haematology
P. 54
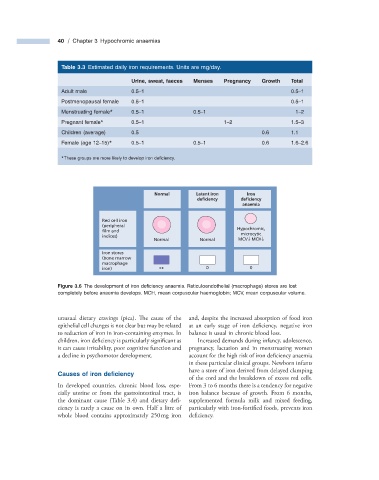
40 / Chapter 3 Hypochromic anaemias
Table 3.3 Estimated daily iron requirements. Units are mg/day.
Urine, sweat, faeces Menses Pregnancy Growth Total
Adult male 0.5 – 1 0.5 – 1
Postmenopausal female 0.5 – 1 0.5 – 1
Menstruating female * 0.5 – 1 0.5 – 1 1 – 2
Pregnant female * 0.5 – 1 1 – 2 1.5 – 3
Children (average) 0.5 0.6 1.1
Female (age 12 – 15) * 0.5 – 1 0.5 – 1 0.6 1.6 – 2.6
* These groups are more likely to develop iron defi ciency.
Normal Latent iron Iron
deficiency deficiency
anaemia
Red cell iron
(peripheral
film and Hypochromic,
microcytic
indices)
Normal Normal MCV↓ MCH↓
Iron stores
(bone marrow
macrophage
iron) ++ 0 0
Figure 3.6 The development of iron defi ciency anaemia. Reticuloendothelial (macrophage) stores are lost
completely before anaemia develops. MCH, mean corpuscular haemoglobin; MCV, mean corpuscular volume.
unusual dietary cravings (pica). The cause of the and, despite the increased absorption of food iron
epithelial cell changes is not clear but may be related at an early stage of iron deficiency, negative iron
to reduction of iron in iron - containing enzymes. In balance is usual in chronic blood loss.
children, iron deficiency is particularly signifi cant as Increased demands during infancy, adolescence,
it can cause irritability, poor cognitive function and pregnancy, lactation and in menstruating women
a decline in psychomotor development. account for the high risk of iron defi ciency anaemia
in these particular clinical groups. Newborn infants
have a store of iron derived from delayed clamping
Causes of i ron d efi ciency
of the cord and the breakdown of excess red cells.
In developed countries, chronic blood loss, espe- From 3 to 6 months there is a tendency for negative
cially uterine or from the gastrointestinal tract, is iron balance because of growth. From 6 months,
the dominant cause (Table 3.4 ) and dietary defi - supplemented formula milk and mixed feeding,
ciency is rarely a cause on its own. Half a litre of particularly with iron - fortified foods, prevents iron
whole blood contains approximately 250 mg iron defi ciency.