Page 52 - Essential Haematology
P. 52
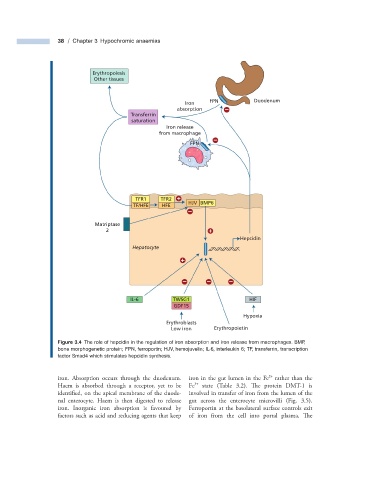
38 / Chapter 3 Hypochromic anaemias
Erythropoiesis
Other tissues
FPN Duodenum
Iron
absorption
Transferrin
saturation
Iron release
from macrophage
FPN
TFR1 TFR2
TF/HFE HFE HJV BMP6
Matriptase
2
Hepcidin
Hepatocyte
IL-6 TWSG1 HIF
GDF15
Hypoxia
Erythroblasts
Low iron Erythropoietin
Figure 3.4 The role of hepcidin in the regulation of iron absorption and iron release from macrophages. BMP,
bone morphogenetic protein; FPN, ferroportin; HJV, hemojuvelin; IL - 6, interleukin 6; TF, transferrin, transcription
factor Smad4 which stimulates hepcidin synthesis.
2 +
iron. Absorption occurs through the duodenum. iron in the gut lumen in the Fe rather than the
3 +
Haem is absorbed through a receptor, yet to be Fe state (Table 3.2 ). The protein DMT - 1 is
identified, on the apical membrane of the duode- involved in transfer of iron from the lumen of the
nal enterocyte. Haem is then digested to release gut across the enterocyte microvilli (Fig. 3.5 ).
iron. Inorganic iron absorption is favoured by Ferroportin at the basolateral surface controls exit
factors such as acid and reducing agents that keep of iron from the cell into portal plasma. Th e